Risk Prediction of End-Stage Renal Disease in Living Kidney Donors.
JHU, Baltimore.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 52
Keywords: Kidney
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Living Kidney Donation: Risk Factors for Adverse Long term Outcome
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Veterans Auditorium
Recent studies have shown inreased risk of end stage renal disease (ESRD) in living kidney donors compared to healthy nondonors. Donors must understand the risk of donation in order to provide informed consent, but the risk of ESRD in individual donors is unknown.
METHODS: Using SRTR data linked to outcome data from CMS, we studied the association between donor age, sex, race, relatedness to recipient, BMI, and ESRD in 120,203 living kidney donors 1987-2014. We used Cox regression with multiple imputation to account for missing data and late entries to account for imperfect ESRD surveillance prior to 1994. We used the model to create a calculator for individual risk prediction.
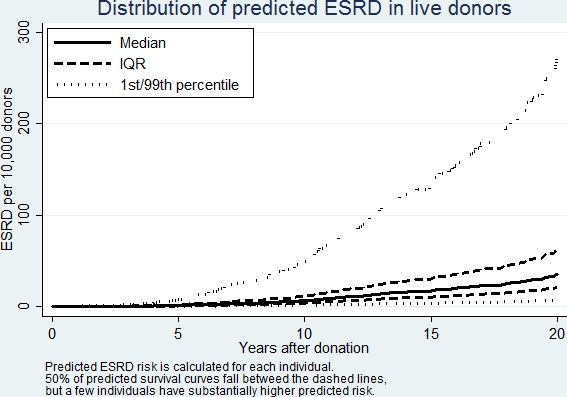
RESULTS: Male donors had 2-fold higher risk of ESRD than female donors (Table). African-American (AA) donors had increased risk compared to non-AA donors; the magnitude of increased risk varied with donor age. Among non-AA donors, older age was associated with increased risk (46% higher risk per 10 years of age, Table), but there was no evidence of increased risk with age among AA donors. Donors with no biological relationship to the recipient had 35% lower risk than donors with a biological relationship . Higher BMI was associated with increased risk (52% higher risk per 5 kg/m2). There was no evidence of association between eGFR and ESRD risk after adjusting for other factors (p=0.9). The c-statistic of the model was 0.71. Among all donors in the study, median predicted risk at 5, 10, and 15 years post-donation was 0.01%, 0.06%, and 0.17%, respectively. Median (IQR) predicted risk of ESRD at 20y was 0.35% (0.21%-0.62%), but 1% of donors had 2.7% or higher predicted risk of ESRD (Figure). Online calculator at transplantmodels.com/donesrd
CONCLUSIONS: Risk of ESRD within 20 years post-donation is small for most donors, but a few donors have greatly increased risk. The online calculator is a useful tool for evaluating and counseling potential kidney donors.
| Risk factor | HR | p |
| Male sex | 1.56 1.99 2.56 | <0.001 |
| AA race (at age 40) | 2.27 3.15 4.37 | <0.001 |
| Age per 10y (non-AA) | 1.23 1.46 1.72 | <0.001 |
| Age per 10y (AA) | 0.63 0.80 1.02 | 0.07 |
| Not related to recipient | 0.63 0.45 0.98 | 0.04 |
| BMI per 5 units | 1.14 1.52 2.03 | <0.01 |
CITATION INFORMATION: Massie A, Chow E, Segev D. Risk Prediction of End-Stage Renal Disease in Living Kidney Donors. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Massie A, Chow E, Segev D. Risk Prediction of End-Stage Renal Disease in Living Kidney Donors. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/risk-prediction-of-end-stage-renal-disease-in-living-kidney-donors/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
