Risk Factors for Failure to Complete Post-Donation Follow-Up among Obese Living Kidney Donors
1Surgery, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
2Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C152
Keywords: Multivariate analysis
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Living Donor Issues
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
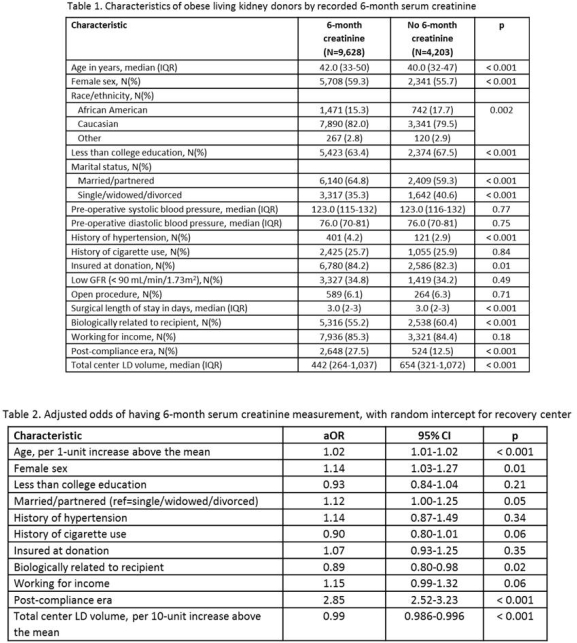
Introduction: Living kidney donors in the United States who were obese at the time of donation are at greater risk of end-stage renal disease than their non-obese counterparts, and may benefit from more intensive post-donation follow-up. Compared to their non-obese counterparts, obese living donors are less likely to have complete follow-up data. It is unknown what factors may be driving greater risk for incomplete follow-up among obese living donors.
Methods: Adult living kidney donors with obesity (body mass index ≥ 30 kg/m2) at donation and reported to the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients from January 2005-July 2015 were included (n=13,831). Donor characteristics were compared based on having a recorded serum creatinine at 6-months post-donation, and multilevel logistic regression models were used to estimate odds of 6-month creatinine measurement, with a random intercept for recovery center.
Results: Obese donors who were older, female, Caucasian, married, had a history of hypertension, and were insured at donation were more likely to have a 6-month serum creatinine recorded on unadjusted analyses; obese donors with less than a college education or those biologically related to their recipient were less likely to have a 6-month serum creatinine. After adjustment, older age, female sex, and donation following the implementation of new center follow-up requirements were associated with higher odds of 6-month creatinine, while lower odds of 6-month creatinine were seen for biologically-related donors and donors at centers with higher total living donor volume.
Conclusion: Obese donors biologically related to their recipient or who donated at a high volume living donor center were less likely to have 6-month follow-up. These findings suggest the need for targeted education and intervention both at the patient and center level to increase follow-up among obese living donors.
CITATION INFORMATION: Reed R., MacLennan P., Shelton B., Mustian M., McWilliams D., Sawinski D., Locke J. Risk Factors for Failure to Complete Post-Donation Follow-Up among Obese Living Kidney Donors Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reed R, MacLennan P, Shelton B, Mustian M, McWilliams D, Sawinski D, Locke J. Risk Factors for Failure to Complete Post-Donation Follow-Up among Obese Living Kidney Donors [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/risk-factors-for-failure-to-complete-post-donation-follow-up-among-obese-living-kidney-donors/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress