Research Publication Rates, Characteristics, and Perceptions of Solid Organ Transplant Pharmacy Residency Training: A Survey of Program Directors
1University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, 2NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY, 3Inova Fairfax Hospital, Falls Church, VA, 4Duke University Hospital, Durham, NC, 5NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, 6Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA, 7UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco, CA, 8UCSD Health, San Diego, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1665
Keywords: Outcome, Resource utilization
Topic: Clinical Science » Pharmacy » 30 - Non-Organ Specific: Clinical Pharmacy/Transplant Pharmacotherapy
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the publication rate of post-graduate year 2 (PGY2) transplant pharmacy residents, to characterize current practices surrounding resident research and to assess characteristics of published abstracts and manuscripts.
*Methods: An international, electronic survey of all PGY2 SOT residency programs was distributed. An invitation for survey participation was sent by email to the residency program directors (RPDs), and information related to the program, director, resident, and each project was gathered for residents graduating between 2016 and 2019. Factors influencing resident publication success were assessed with multivariate logistic regression modeling.
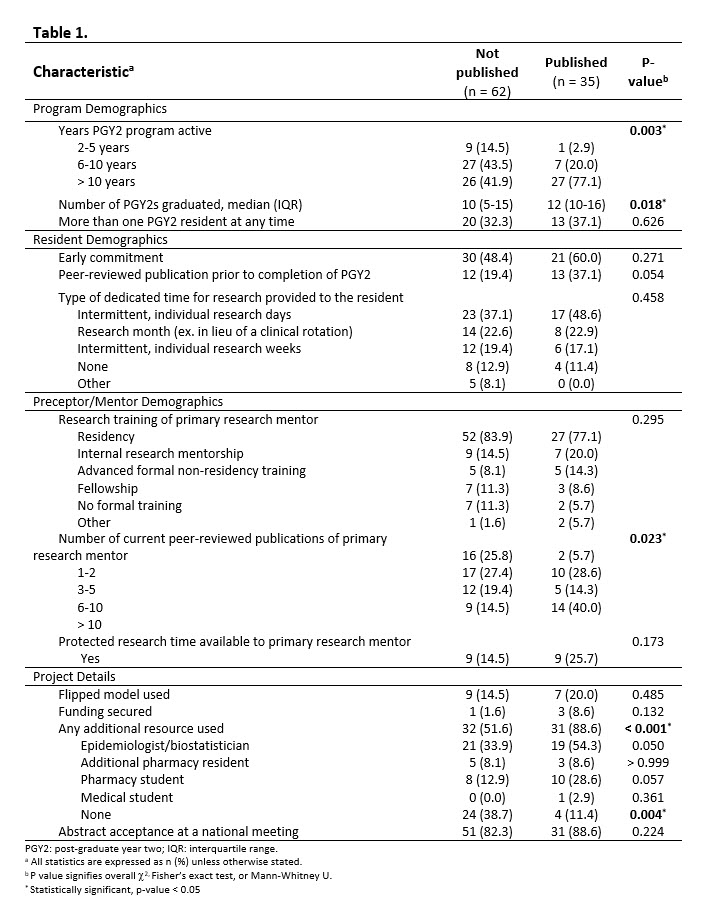
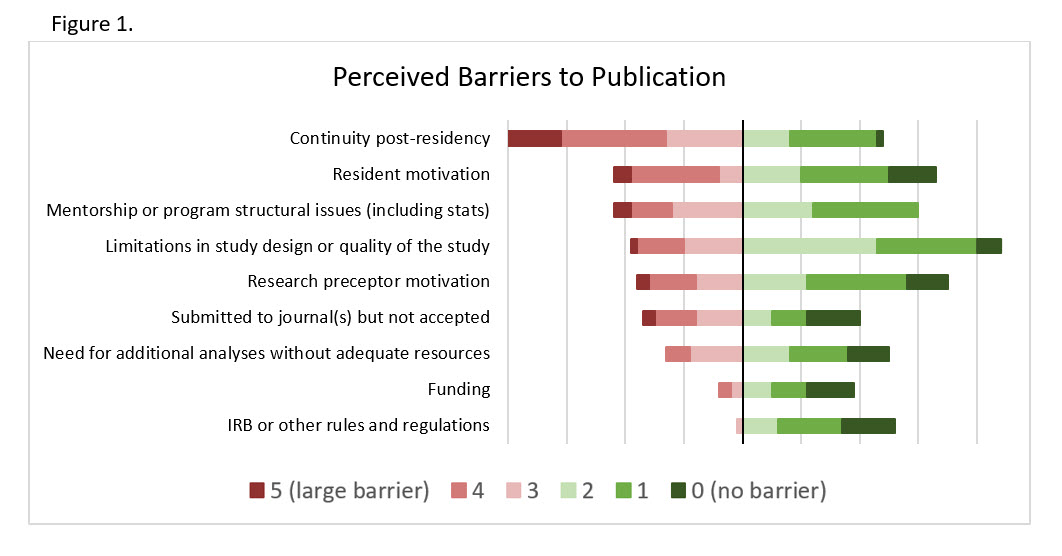
*Results: A total of 38 RPD responses were analyzed (response rate was 67.8%). All PGY2 programs were ASHP accredited, 92% were at academic medical centers, and more than 80% of programs have been active over 6 years with a median of 10 (IQR 5, 13) graduated residents. 36.1% of SOT PGY2 research projects were published, 22.4% intend to submit or have a manuscript under revision, and 38.7% will not pursue publication. RPDs commonly rated their programs as “effective” or “extremely effective” (50.0%) in enabling publication. Of published projects, 81% were in medical journals and 19% in pharmacy journals. Median impact factor was 2.9 (IQR 1.5, 2.9). Factors more commonly reported for published projects are listed in Table 1. Perceived barriers to publication are listed in Figure 1. Utilization of additional resources was independently predictive of publication [OR=5.8; 95% CI 1.3, 26.8), p=0.023].
*Conclusions: Despite program confidence to achieve publishable research, publication rates were only 36.1%. Maximizing additional resources helps to accomplish publication within these training programs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Melaragno J, Kovac D, Witek S, Harris M, Khalil K, Laub M, Quan D, Lichvar A. Research Publication Rates, Characteristics, and Perceptions of Solid Organ Transplant Pharmacy Residency Training: A Survey of Program Directors [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/research-publication-rates-characteristics-and-perceptions-of-solid-organ-transplant-pharmacy-residency-training-a-survey-of-program-directors/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress