Repeat-Pancreas Transplant after Pancreas Graft Failure in Simultaneous Pancreas and Kidney Transplants is Associated with Better Kidney Graft Survival
University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 199
Keywords: Pancreas transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics I
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Location: Room 209
*Purpose: Simultaneous pancreas and kidney (SPK) transplant is usually the best option for the diabetic ESRD patient. But there is limited information about kidney graft outcomes in SPK recipients with isolated pancreas graft failure who do or do not undergo repeat pancreas transplantation.
*Methods: We analyzed our primary SPK recipients transplanted between 01/2000 and 12/2016 who experienced pancreas graft failure yet retained kidney graft function. Patients were divided into two groups based on whether they underwent repeat pancreas transplant (Re-Ptx+) or not (Re-Ptx-). Patients were excluded if the repeat pancreas graft survival was less than 30 days. Kidney graft function and survival were the primary endpoints.
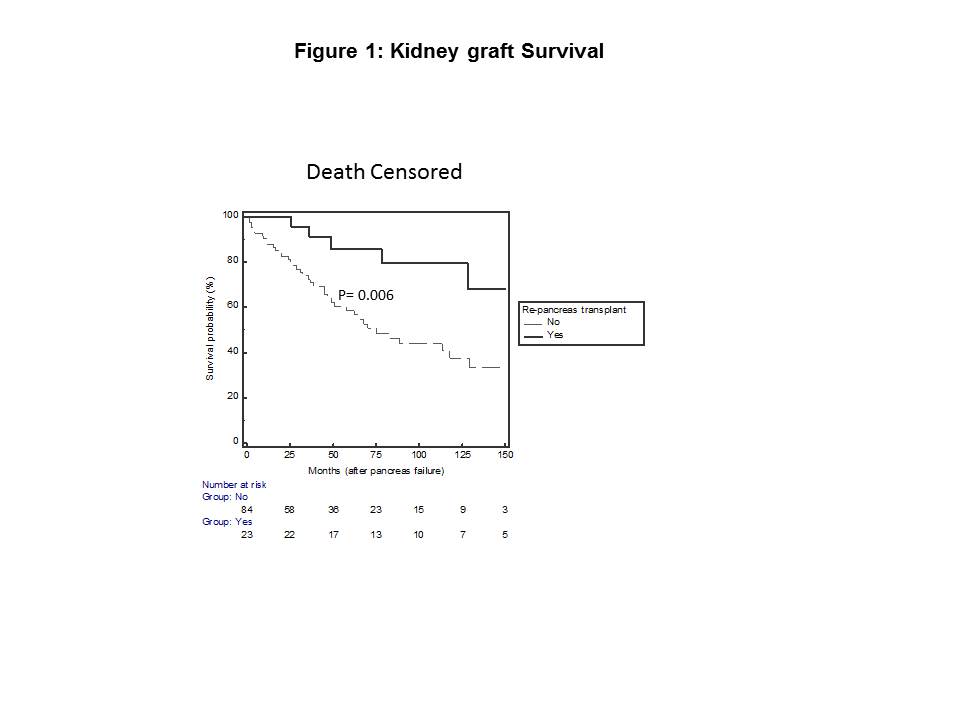
*Results: 107 patients satisfied our selection criteria, 23 in Re-Ptx+ and 84 in Re-Ptx-. Most patients in both groups were male and Caucasian. Mean interval from SPK to pancreas failure was significantly shorter in the Re-Ptx+ compared to the Re-Ptx- group, 16.0 ± 31.9 vs 45.7 ± 47.0 months (p=0.005) respectively. There was no significant difference in kidney graft follow up post SPK between two groups (p=0.38). At last follow up, kidney graft failure was significantly higher in the Re-PTx- group compared to the Re-PTx+ group, 67% vs 43 % (p=0.04). Death-censored kidney graft failure was also higher in the Re-PTx- group, 48% vs 26% (p=0.06). In Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, kidney graft survival probability was significantly lower in the Re-PTx- group (Figure 1). A similar pattern was seen after 1:1 matching for the interval between SPK and pancreas graft failure. The Re-Ptx+ and Re-PTx- groups had similar eGFR and serum creatinine at last follow up.
*Conclusions: In SPK recipients with pancreas graft failure, repeat pancreas transplant after pancreas graft failure is associated with better kidney graft survival. Even though Re-PTx patients take the risks associated with repeat pancreas surgery, the provider should discuss this option.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parajuli S, Arunachalam A, Swanson K, Aziz F, Garg N, Redfield R, Kaufman D, Djamali A, Odorico J, Mandelbrot D. Repeat-Pancreas Transplant after Pancreas Graft Failure in Simultaneous Pancreas and Kidney Transplants is Associated with Better Kidney Graft Survival [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/repeat-pancreas-transplant-after-pancreas-graft-failure-in-simultaneous-pancreas-and-kidney-transplants-is-associated-with-better-kidney-graft-survival/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress