Renal Function Outcomes by HLA Mismatch in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving Everolimus PlusReduced-Dose Cyclosporine versus Mycophenolate Plus Standard-Dose Cyclosporine: 24-Month Subanalysis of A1202 Study.
1Kitasato University, Sagamihara, Japan
2Nagoya Daini Red Cross Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
3Ichikawa General Hospital, Tokyo Dental College, Ichikawa, Japan
4Novartis Pharma K.K., Tokyo, Japan
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D81
Keywords: HLA matching, Kidney transplantation, Proteinuria, Renal function
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Purpose: High levels of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatches are a key determinant of kidney allograft survival. Here, we present 24-month (M) subanalysis of the A1202 study wherein influence of HLA mismatch on renal function outcomes was compared in kidney transplant recipients (KTxRs) receiving everolimus (EVR) plus reduced-dose cyclosporine (rCsA) vs mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus standard-dose CsA (sCsA).
Methods: A1202 was a 12M core plus 12M extension follow-up, multicenter, open-label study comparing efficacy and safety of 1.5 mg/day EVR plus rCsA (EVR+rCsA) vs 2 g/day MMF plus sCsA (MMF+sCsA) in Japanese de novo KxTRs. Patients completing the core and extension follow-up were included in this subanaylsis (n=50 each arm). Renal function [eGFR by MDRD, serum creatinine, and creatinine clearance] and composite efficacy failure events [treated biopsy-proven acute rejection, graft loss, death, or loss to follow-up] were determined at M24 in HLA mismatch groups (<3 vs ≥3).
Results: KTxRs were categorized by treatment and level of mismatch into 4 groups (Table). Although treatment differences were not statistically significant, mean eGFR remained numerically higher in EVR+rCsA vs MMF+sCsA arm for both mismatch groups up to M24 (<3: 60.1 vs 56.8 mL/min/1.73m2, P=0.51; ≥3: 62.1 vs 56.4 mL/min/1.73m2; P=0.24). Serum creatinine levels and creatinine clearance were similar in both arms for both mismatch groups. More KTxRs in EVR+rCsA vs MMF+sCsA arm (18.8% vs 8.1%) had sub-nephrotic proteinuria for mismatch group ≥3, whereas more KTxRs in MMF+sCsA arm had sub-nephrotic proteinuria for mismatch group <3. Composite efficacy failure events were comparable in both arms for both mismatch groups. No new safety signals were noted.
Conclusion: These results suggest that renal function outcomes are similar up to 24 months in KTxRs receiving EVR+rCsA vs MMF+sCsA regardless of HLA mismatch level.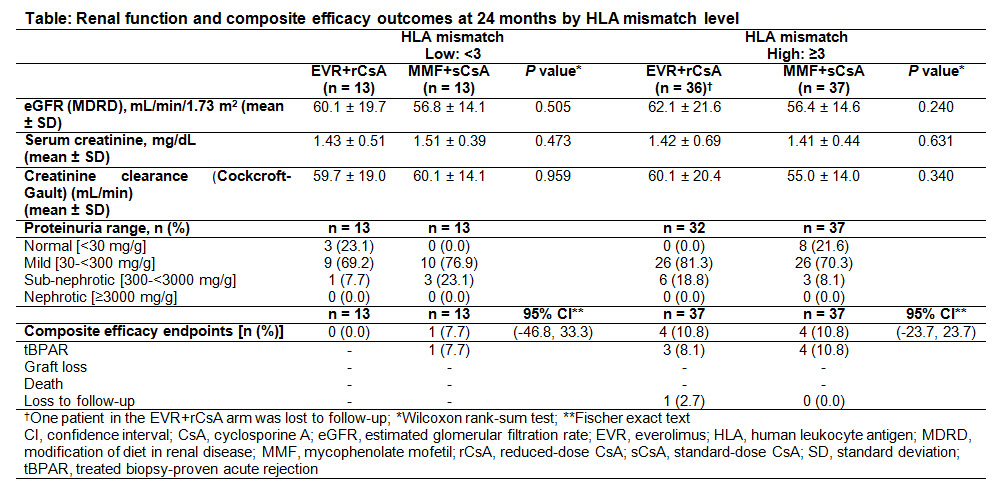
CITATION INFORMATION: Yoshida K, Watarai Y, Nakagawa K, Kamisawa O. Renal Function Outcomes by HLA Mismatch in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving Everolimus PlusReduced-Dose Cyclosporine versus Mycophenolate Plus Standard-Dose Cyclosporine: 24-Month Subanalysis of A1202 Study. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoshida K, Watarai Y, Nakagawa K, Kamisawa O. Renal Function Outcomes by HLA Mismatch in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving Everolimus PlusReduced-Dose Cyclosporine versus Mycophenolate Plus Standard-Dose Cyclosporine: 24-Month Subanalysis of A1202 Study. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/renal-function-outcomes-by-hla-mismatch-in-de-novo-kidney-transplant-recipients-receiving-everolimus-plusreduced-dose-cyclosporine-versus-mycophenolate-plus-standard-dose-cyclosporine-24-month-subana/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
