Reducing Financial Burden for Living Donors: A Single Center Experience of Increased National Living Donor Assistance Center (NLDAC) Support
Transplant Center, University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 605
Keywords: Economics, Employment, Living donor, Resource utilization
Topic: Administrative » Administrative » 01 - Quality Assurance Process Improvement & Regulatory Issues
Session Information
Session Name: Quality Assurance Process Improvement & Regulatory Issues
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: National Living Donor Assistance Center (NLDAC) offers assistance to overcome some of the financial barriers associated with Living Donation. From 2015 to 2020, an average of 13% of living donor (LD) surgeries were NLDAC supported at our institution. Beginning in March 2021, an internal review of the NLDAC process revealed deficits in utilization and process improvement was undertaken.
*Methods: With the overarching goal of increasing NLDAC utilization, our center’s Social Work Department identified the following areas for growth: screening/tracking, communication, and education. A tracking tool was integrated into the existing screening process that determined donor/recipient pair eligibility; this tool assisted the newly designated “NLDAC Team” consisting of 2 Social Workers (SW) and an assistant in approaching the NLDAC process as a team. The NLDAC Team participates in twice weekly huddles where the tracking tool is reviewed and timely submission of applications prioritized. The NLDAC team sought to increase proactive communication with LD team by creating a NLDAC distribution list, creating a single point of contact. Transparency between the LD and NLDAC team was improved with sharing of the tracking tool and surgical calendars. With the knowledge that a donor was eligible for NLDAC, SW focused on integrating individualized education about NLDAC’s program into donor assessment. SW enhanced the NLDAC application process to minimize the need for printed documents and make electronic completion easier. In consideration of NLDAC process improvement (PI) sustainability, all members of the Social Work Department received training on integration of NLDAC into SW assessment. A review of NLDAC utilization was introduced during Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement (QAPI) to educate stakeholders and allow for feedback.
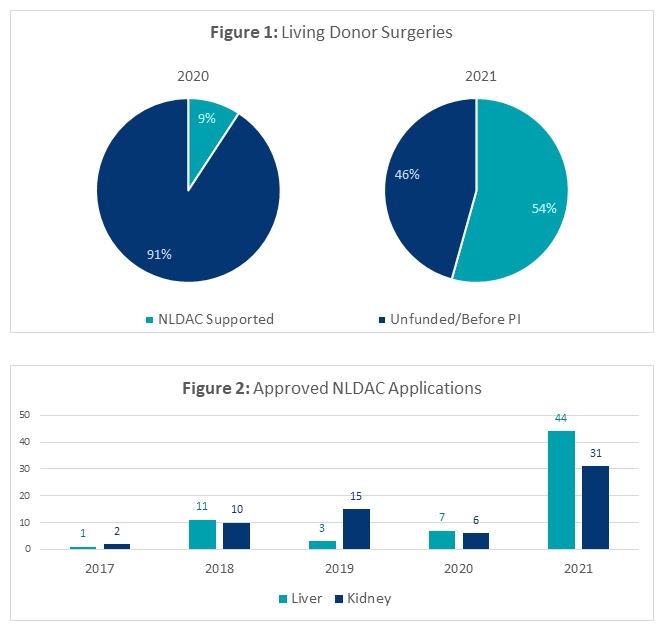
*Results: With directed efforts and improved communication with the multidisciplinary team, our center increased NLDAC utilization six-fold. From the beginning of the NLDAC PI in March 2021 through October 2021, 54% of LD surgeries were NLDAC supported compared to only 9% in 2020; most unfunded surgeries were either ineligible for assistance or completed before PI implementation (Figure 1). 75 NLDAC applications have been approved in 2021 compared to only 13 in 2020 (Figure 2).
*Conclusions: NLDAC utilization can be increased by directed efforts by Transplant centers, which should review their internal processes to ensure they are meeting the needs of their LD population and reducing their financial burden.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Klair T, Throgmorton K, Oviedo D, Cepeda E. Reducing Financial Burden for Living Donors: A Single Center Experience of Increased National Living Donor Assistance Center (NLDAC) Support [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/reducing-financial-burden-for-living-donors-a-single-center-experience-of-increased-national-living-donor-assistance-center-nldac-support/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress