Reduced Health Literacy in Kidney Transplant Recipients May Be Associated with Difficulty Identifying a Live Kidney Donor
Transplant Center, Vanderbilt, Nashville
Surgery, Vanderbilt, Nashville
Biostatistics, Vanderbilt, Nashville
Anesthesiology, Vanderbilt, Nashville
Nephrology, Vanderbilt, Nashville
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 524
Introduction: Health literacy (HL) may be a mediator for known socioeconomic (SES) and racial disparities in live kidney donation and provide a target for interventions to increase living donation. We evaluated the associations of demographic characteristics with HL in live kidney donors (LD), living donor recipients (LDR), and deceased donor recipients (DDR).
Methods: A single center retrospective review of patients undergoing kidney donation or transplantation between September 2010 and July 2012 was performed. Demographic data (race, age, educational attainment) and HL (reported via 3 validated brief screening questions at admission; (range 3-15) classified high=15, moderate=9-14, low<=8) were collected. Chi-square and logistic regression models were used to test factors associated with reduced HL.
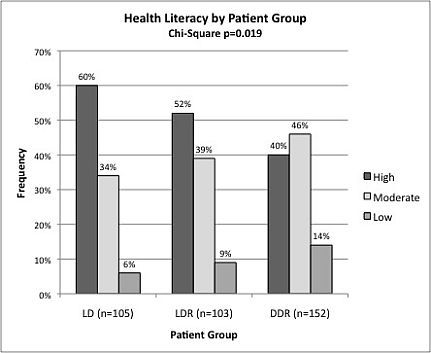
Results: The sample included 360 adults (105 LD, 103 LDR, 152 DDR; 46±14 yrs; 70% white; 56% male; 14±3 education yrs). The distribution of HL categories differed significantly among the 3 groups (p=0.019, Figure). HL scores were skewed (49% high, 41% moderate, 10% low). After controlling for age, race, and education, DDR were more likely to have moderate or low HL than LD. The likelihood did not differ between LDR and LD.
| Variable | Β | OR | OR 95% CI | p-value |
| Age (yrs) | 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.99, 1.02 | 0.536 |
| Education (yrs) | -0.29 | 0.75 | 0.68, 0.83 | <0.001 |
| Race (ref=white) | 0.43 | 1.54 | 0.93, 2.55 | 0.095 |
| LDR (ref=LD) | 0.05 | 1.05 | 0.57, 1.92 | 0.873 |
| DDR (ref=LD) | 0.67 | 1.95 | 1.08, 3.53 | 0.028 |
Conclusions: After accounting for demographic factors known to influence access to living kidney donation, DDR were more likely to have reduced HL. Screening transplant candidates for reduced HL may identify those with greater difficulty identifying a live donor. Future interventions targeted at transplant candidates with literacy-related factors (race, SES, social support) and reduced HL may increase live donation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dageforde L, Petersen A, Harms K, Feurer I, Ehrenfeld J, Cavanaugh K, Moore D. Reduced Health Literacy in Kidney Transplant Recipients May Be Associated with Difficulty Identifying a Live Kidney Donor [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/reduced-health-literacy-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-may-be-associated-with-difficulty-identifying-a-live-kidney-donor/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
