Quality of Life After Islet/Pancreas Transplantation in Insulin Dependent Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature.
I. Mosca1, S. Knight2, S. Mittal3, P. J. Friend1
1Nuffield Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Oxford, Oxford Transplant Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2Nuffield Department of Surgical Sciences, Simon Knight, Oxford, United Kingdom, 3Nuffield Department of Surgical Sciences, Shruti Mittal, Oxford, United Kingdom
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D291
Keywords: Outcome, Psychosocial, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: To investigate the current literature on Quality of Life after Islet and Pancreas Transplantation in Insulin Dependent Diabetic Patients with or without renal failure.
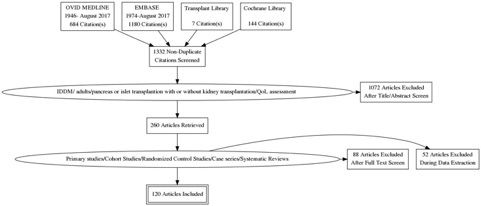
*Methods: This systematic review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviewes and Meta-Analysis framework.(PRISMA).Relevant databases were searched (OVID MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Transplant Library and the Cochrane Library) for studies reporting disease-specific or generic quality of life outcomes in adult insulin dependent diabetic patients undergoing pancreas or islet transplantation. All primary study types and systematic reviews were considered. Two independent reviewers screened the search results and differences were resolved by discussion. Demographic details, outcomes and details of PROMs used were extracted and analysed.
*Results: The initial searches identified 2015 potentially relevant references. Following removal of duplicates and abstract screening, the full text of 260 studies was reviewed, yielding a total of 120 manuscripts from 574 studies meeting the inclusion criteria.The most common generic health status questionnaire adopted was the Short-Form 36 (SF-36). The great majority of studies on QoL after IT included also a disease specific questionnaire, most commonly The Hypoglycaemia fear Survey (HFS) or the Diabetes Quality of Life Questionnaire (DQOL).
These preliminary findings are part of a broader analysis on QOL outcomes of pancreas and islet transplant, using comparative data where appropriate.
*Conclusions: Quality of life in patients with diabetes can be significantly compromised by metabolic and long term complications of the disease. Pancreas Transplantation and Islet Transplantation are therapeutic options for a selected cohort of people with insulin dependent diabetes.It is common agreement that surgical risks related to transplantation must be weighted against potential long-term benefits as well as the patients’s own preference. Clinical outcomes are well documented, whilst the quality of life benefits associated with pancreas transplantation are less known. In the last two decades much has changed in the methodology of Quality of Life studies. This systematic review offers the opportunity to investigate QoL outcomes in Pancreas and Islet Transplant recipients as described throughout the years, and to identify the most appropriate Patient Reported Outcomes Measures (PROMs) for use in future clinical trials in this patient population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mosca I, Knight S, Mittal S, Friend PJ. Quality of Life After Islet/Pancreas Transplantation in Insulin Dependent Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/quality-of-life-after-islet-pancreas-transplantation-in-insulin-dependent-diabetic-patients-a-systematic-review-of-the-literature/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress