Probability of Developing Chronic Kidney Disease 1 Year after Living Donor Nephrectomy Correlates with Baseline Kidney Volume and Function
University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 222
Keywords: Donation, Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), Renal dysfunction
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Living Donation: Donor and Recipient Outcomes
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Room 6E
Purpose: Living kidney donor outcomes are tremendously important, especially given expanding donor eligibility. Relative to other predictors, the relationship between remaining kidney volume and post-donation renal function is poorly understood.
Methods: We determined associations between remaining kidney volume (via pre-donation CT angiography) indexed to body surface area (BSA) and 1-year post-donation renal function in 152 living kidney donors at an academic center using multivariable linear and logistic regression for continuous eGFR and chronic kidney disease (CKD, eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73m2), respectively.
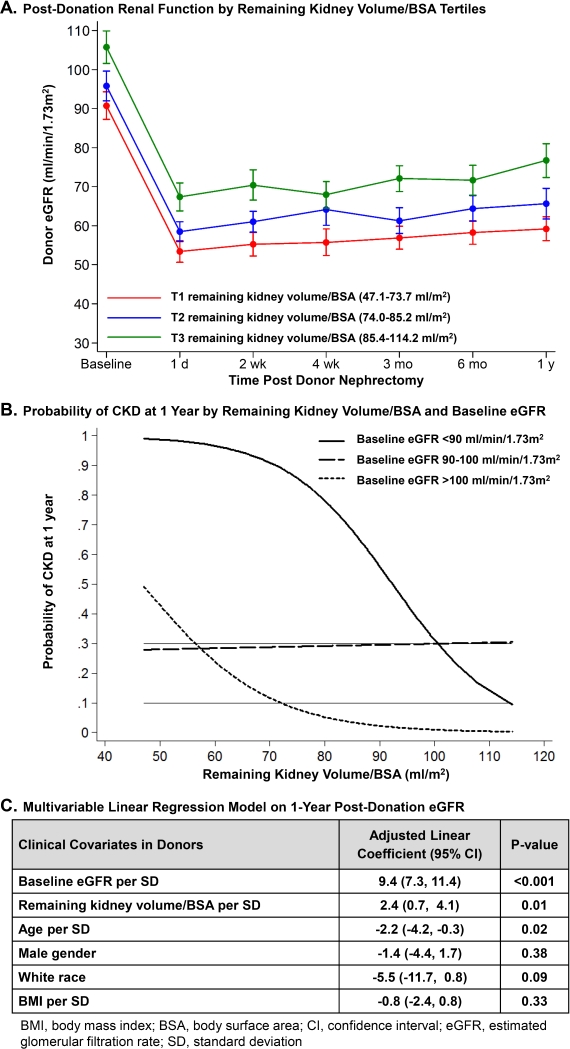
Results: Mean±SD age, body mass index and baseline eGFR were 38±11 y, 26±4 kg/m2 and 97±16 ml/min/1.73m2. 50% were male and 94% were white. Median (range) remaining kidney volume/BSA was 79.6 (47.1-114.2) ml/m2. Mean baseline (pre-donation) eGFR was greater with increasing tertiles (T1-T3) of remaining kidney volume/BSA (92±14, 97±16 and 107±16 ml/min/1.73m2 for T1, T2 and T3, respectively; p<0.001). There were no other significant differences in baseline characteristics by remaining kidney volume/BSA tertiles. As shown in the Figure (panel A), post-donation renal function declined and then remained separated throughout the first year for T1-T3. Panel B shows that the probability for CKD at 1-year increased abruptly for lower remaining kidney volume/BSA in donors with baseline eGFR <90 ml/min/1.73m2, remained stable at around 30% regardless of remaining kidney volume/BSA in donors with baseline eGFR 90-100 ml/min/1.73m2, and did not increase above 30% unless remaining kidney volume/BSA was <55 ml/m2 in donors with baseline eGFR >100 ml/min/1.73m2. As shown in panel C, each SD increase in remaining kidney volume/BSA was associated with 2.4 (95% CI: 0.7-4.1) ml/min/1.73m2 higher adjusted 1-year eGFR.
Conclusions: In this living donor cohort, remaining kidney volume/BSA was a major determinant for CKD 1 year after nephrectomy in those with baseline eGFR <90 ml/min/1.73m2. More studies are needed to evaluate the predictive utility of this clinical measure and its potential role in donor evaluations and informed consent.
CITATION INFORMATION: Hall I., Shaaban A., Beddhu S., Shihab F. Probability of Developing Chronic Kidney Disease 1 Year after Living Donor Nephrectomy Correlates with Baseline Kidney Volume and Function Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hall I, Shaaban A, Beddhu S, Shihab F. Probability of Developing Chronic Kidney Disease 1 Year after Living Donor Nephrectomy Correlates with Baseline Kidney Volume and Function [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/probability-of-developing-chronic-kidney-disease-1-year-after-living-donor-nephrectomy-correlates-with-baseline-kidney-volume-and-function/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress