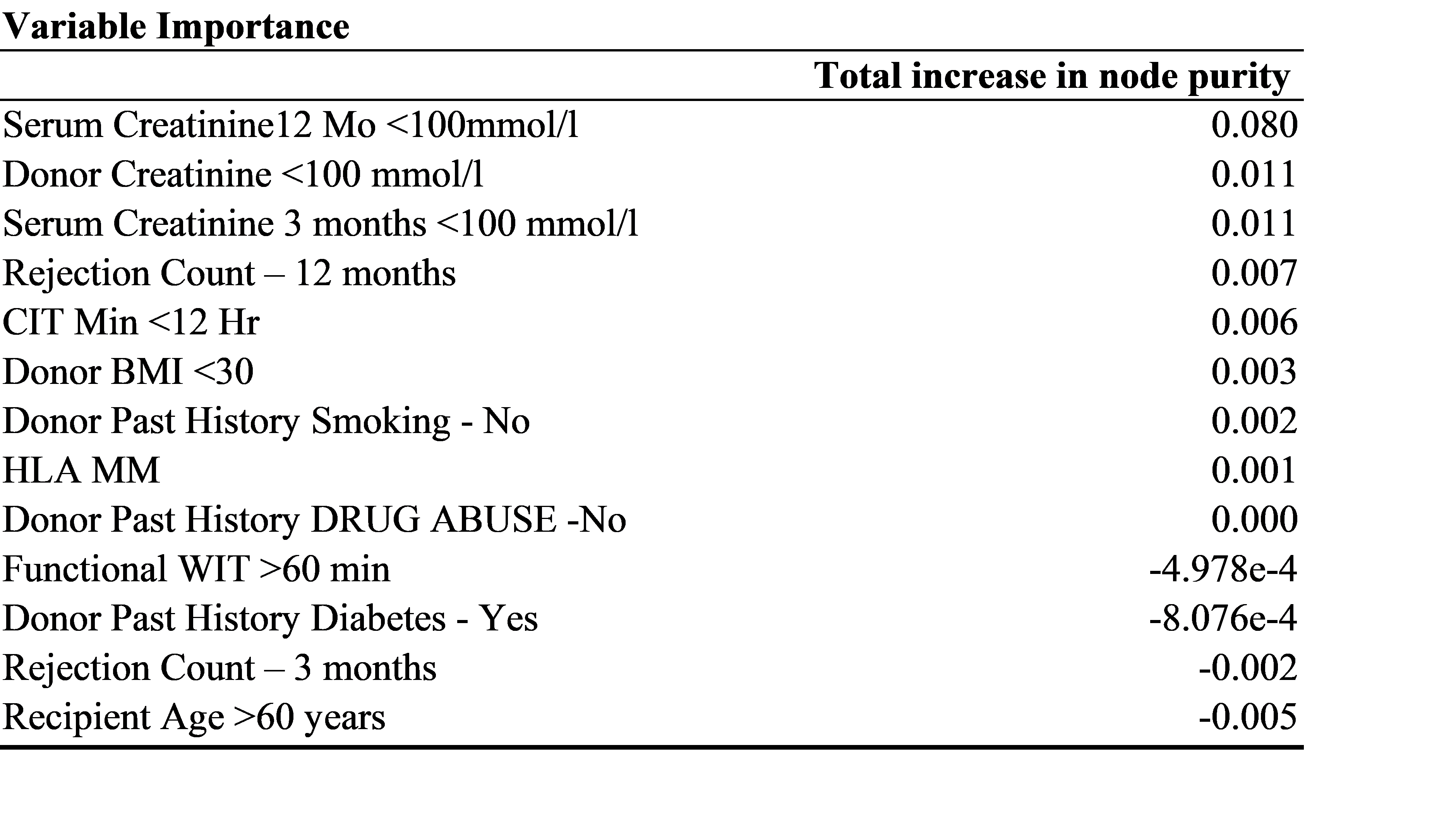Predictors of Short and Long Term Outcomes of Donor After Cardiac Death (DCD) versus Donor After Brain Death (DBD) Kidney Transplantation from Supra Marginal Donors ( D4). A Machine Learning Analysis (MLA) of NHSBT Registry Data Since Year 2000
H. Sharma1, A. Sharma2, T. Gunawardhane1, B. Devkaran1, K. Kapoor1, S. Mehra1
1Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool, United Kingdom, 2Loyola University Chicago, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1803
Keywords: Donors, marginal, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Organ Inclusive » 72 - Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Social Media in Transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Social Media in Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Marginal Donor 4- D4 ( Donor Risk Index ≥1.50 ) Matching was introduced as a part of new Kidney allocation scheme in the UK in 2018. The focus is primed at recipient matching but the role of types of transplant for these donors is unreported. The aim of our study is to assess predictors associated with survival outcomes for DCD and DBD transplants from D4 Donors.
*Methods: We harmonized the NHSBT Data to shortlist the D4 criteon kidneys. The Predictors of Transplant outcomes were evaluated by five classifiers including logistic regression, SVM, random forest, K-Nearest neighbour matching and adaptive boosting . Random Forest Model had the best performance validated by RMSE. Survival outcomes and predictors data mined from MLA were further mined with Cox Regression.
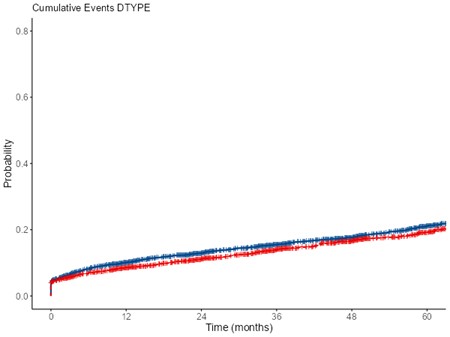
*Results: 6254 D4 donors had 3793 (DBD) and 2461 ( DCD) Kidney transplantation between 2000 -2018.. The Odds of DGF and PNF in DCD Kidneys was significant ( 1.7 (1.5-1.44) p <0-001, 1.2( 1.1- 1.6) p=0.02 respectively. There were minor but statistically insignificant difference in regional outcomes across the UK. The Model used 70% of data for testing, 15% for validation and 15% for testing. The Validation accuracy was 91% and testing accuracy was 83.%, AUC was 0.714. In regards to survival at 3 & 5 years post transplant, Serum Creatinine >100 mmol/L at 12 months, Donor Creatinine <100 mmol/l at procurement, Serum Creatinine >100 mmol/L at 3 months, no rejection within 12 months and CIT <12 hrs were the variable of importance in order. The 1,3,5 year survival for DBD versus DCD transplants was 90%, 85%, 81%; 89, 84%, 80% respectively
*Conclusions: The MLA accurately predicts variable of importance. There is no statistical difference in DCD verus DBD transplant survival outcomes for D4 kidneys though DCD kidneys with CIT >12 hrs do have a significant risk of DGF and PNF.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sharma H, Sharma A, Gunawardhane T, Devkaran B, Kapoor K, Mehra S. Predictors of Short and Long Term Outcomes of Donor After Cardiac Death (DCD) versus Donor After Brain Death (DBD) Kidney Transplantation from Supra Marginal Donors ( D4). A Machine Learning Analysis (MLA) of NHSBT Registry Data Since Year 2000 [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/predictors-of-short-and-long-term-outcomes-of-donor-after-cardiac-death-dcd-versus-donor-after-brain-death-dbd-kidney-transplantation-from-supra-marginal-donors-d4-a-machine-learning-analysis/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress