Prediction of Post-Operative Length of Stay and Unplanned Reoperation in Patients Transplanted for Alcoholic Liver Disease: An Artificial Neural Network Approach
Surgery, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C133
Keywords: Outcome, Post-operative complications
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Liver Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Purpose:
Using artificial neural network (ANN) modeling, this study aims to optimize the prediction of prolonged length of stay (LOS) and need for unplanned reoperation (UR) in patients transplanted for alcoholic liver disease.
Methods:
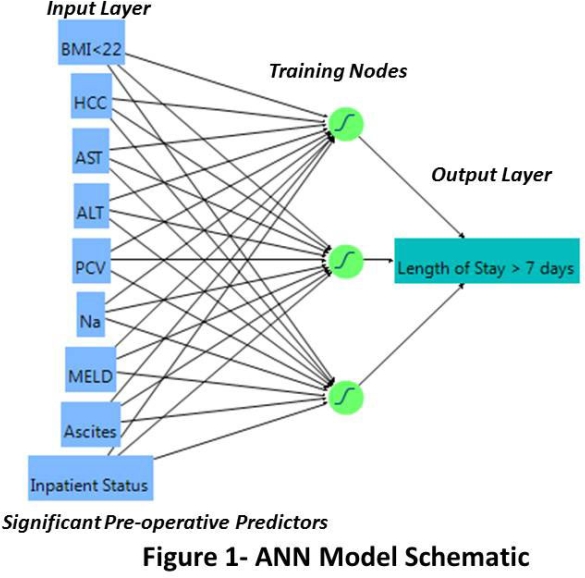
250 patients receiving a primary orthotopic liver transplant (OLT) were analyzed for factors associated with prolonged LOS and UR in both univariate and multivariate analysis (P<.05). Both outcomes were estimated from their significant predictor variables, using multiple logistic regression (MLR) and a 3-node back-propagation ANN (Schematic, Figure 1). Both models were assessed via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and Actual vs. Predicted outcomes plots, with area under the curve (AUC) and Pearson correlation coefficient (r2) as measures of each model's discriminant ability.
Results:
Pre-operative factors carried to multivariate analysis for LOS>7 days and UR are summarized in Table 1. For MLR, AUC values were .7103±.04 and .6837±.06 and r2 values were .1334 and .0869, for endpoints of LOS > 7 days and UR, respectively. For ANN analysis, AUC values of the training set-derived ROC curves (a random 80% of the patients; 20% withheld for internal validation) were 8270±.04 and .7487±.05, and r2 values were .3819 and .1302, for endpoints of LOS>7 days and UR, respectively. The ANN-Training Set ROC curve was superior to that derived via MLR, for the endpoint LOS > 7 days (P=.03).
| Variable | P value (LOS>7d.) | P value (UR) |
| BMI<22 | .0122* | – |
| HCC | .0286*# | .0911# |
| AST | .0138*# | – |
| ALT | .0093*# | – |
| PCV | .0007*# | .0051*# |
| RDW | .0023^ | .0121^ |
| [Na] | .0365*# | – |
| MELD | .0025* | .0022 |
| Ascites | .0267* | .0204 |
| Inpatient | .0005* | .0011 |
Conclusions:
In post-OLT patients with, among other factors, BMI<22, visible ascites, inpatient status and high MELD, a prolonged LOS and need for UR are more likely. Using an ANN, these endpoints can be prognosticated with optimal accuracy, providing improved anticipatory guidance for the patient and physician.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wise E, Williamson K, Hocking K. Prediction of Post-Operative Length of Stay and Unplanned Reoperation in Patients Transplanted for Alcoholic Liver Disease: An Artificial Neural Network Approach [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/prediction-of-post-operative-length-of-stay-and-unplanned-reoperation-in-patients-transplanted-for-alcoholic-liver-disease-an-artificial-neural-network-approach/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
