Pre-Transplant Panel Reactive T Cells (PRT) with IL-15 as a Risk-Stratifier of Acute Rejection in Kidney Transplant Patients on Belatacept Therapy.
1Dept of Medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York
2Dept of Immunology, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland
3Dept of Surgery, Emory University, Atlanta
4Renal Division, UAB, Birmingham
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D126
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
While kidney transplant recipients treated with bela without calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) have better 5-10y eGFR versus those on CNI, Belatacept (bela) use is associated with a high incidence of acute rejection (AR). Donor-reactive CD28neg memory T cells (Tmem) are resistant to CTLA-4Ig and may contribute to AR in patients taking bela. Quantifying these cells pre-transplant may identify subjects at highest risk for developing AR in subjects receiving bela.
We studied stored pre-transplant peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from the CTOT16 study, in which kidney transplant recipients were randomized to induction with rabbit anti thymocyte globulin plus maintenance therapy withMMF and CNI alone (n=15), bela (N=15) or bela+20 weeks of CNI (n=6). We performed IFNg PRT ELISPOT assays using 6-8 EBVneg B cell stimulators +/- IL-15 (required for CD28neg Tmem IFNg-production: Traitanon et al AJT 2014) and tested associations between PRT +/- IL-15 results and AR in the treatment groups. To increase power, we combined the groups receiving bela +/- CNI together (N=21).
Baseline clinical characteristics did not differ between groups. PRTs without IL-15 did not differ between groups. Adding IL-15 augmented PRT responses in the majority of subjects (Panel A). The analysis showed a strong trend toward a higher incidence of AR in samples from subjects in the bela arms in which IL-15-induced >130% increase in pre-transplant PRT vs. the samples in the bela arms without an IL-15-induced increase (75 vs. 27.3%, Panel B). IL-15 PRT did not differentiate AR in the CNI control arm.
Together with previously published findings and acknowledging the small sample-size study, our data suggest that the IL-15-enhanced PRT can detect bela-resistant, CD28neg Tmem and that pre-transplant IL-15 assays could potentially be used to detect subjects at risk for AR when treated with bela.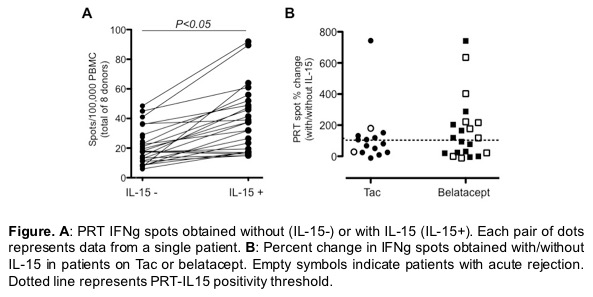
CITATION INFORMATION: Cravedi P, Gandolfini I, Donadei C, Fairchild R, Newell K, Mannon R, Heeger P, CTOT16 Consortium Pre-Transplant Panel Reactive T Cells (PRT) with IL-15 as a Risk-Stratifier of Acute Rejection in Kidney Transplant Patients on Belatacept Therapy. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cravedi P, Gandolfini I, Donadei C, Fairchild R, Newell K, Mannon R, Heeger P, Consortium CTOT16. Pre-Transplant Panel Reactive T Cells (PRT) with IL-15 as a Risk-Stratifier of Acute Rejection in Kidney Transplant Patients on Belatacept Therapy. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pre-transplant-panel-reactive-t-cells-prt-with-il-15-as-a-risk-stratifier-of-acute-rejection-in-kidney-transplant-patients-on-belatacept-therapy/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
