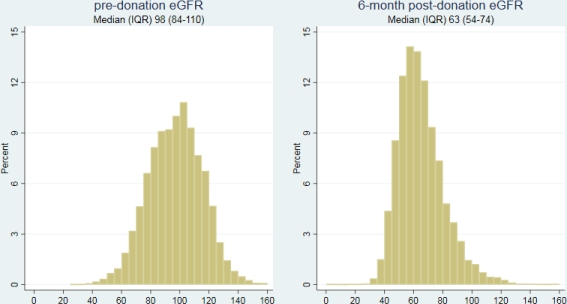
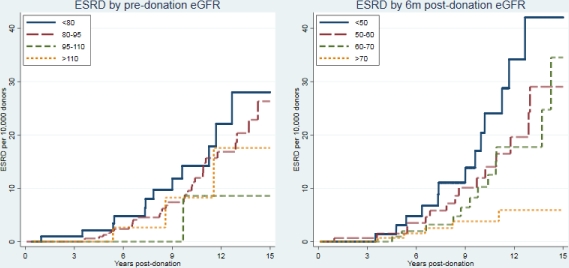
Pre-Donation eGFR, Early Post-Donation eGFR, and Subsequent ESRD Risk in Living Kidney Donors
1Johns Hopkins, Baltimore
2SRTR, Minneapolis.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 336
Keywords: Donation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:42pm-5:54pm
Presentation Time: 5:42pm-5:54pm
Location: Room 6A
The relationship between predonation eGFR and long-term risk of postdonation ESRD has not been characterized. Moreover, while transplant centers are required to collect postdonation serum creatinine (SCr) in donors, the clinical utility of measuring early post-donation renal function is unknown.
METHODS: Using SRTR data, we studied ESRD risk in 66,052 LKDs 1999-2015 who were ESRD-free 9 months post-donation and had at least one SCr reported to the registry between 3 and 9 months post-donation (6m-post eGFR), using Cox regression and adjusting for donor age, sex, race (black vs all other), 1st-degree biological relationship to recipient, and BMI. Predonation eGFR and 6m-post eGFR were calculated using the CKD-EPI equation.
RESULTS: Donor eGFR declined from median (IQR) 98 (84-110) mL/min/1.73 m2 predonation to 63 (54-74) mL/min/1.73 m2 6m-post (Figure 1). A 10-unit increase in predonation eGFR was associated with 17% decreased risk of ESRD (aHR=0.70 0.83 0.99, p=0.04) (Figure 2). In a separate model, a 10-unit increase in 6m-post eGFR was associated with 40% decreased risk of ESRD (aHR=0.46 0.60 0.79, p<0.001) (Figure 2). In a combined model, the association between predonation eGFR and ESRD risk disappeared (aHR per 10u=0.79 0.98 1.21, p=0.9) while the association between 6m-post eGFR and ESRD risk remained the same (aHR per 10u=0.44 0.61 0.83, p<0.001), suggesting that the association between predonation eGFR and ESRD is fully mediated by 6m-post eGFR.
CONCLUSIONS: Both predonation and 6m-post eGFR are inversely associated with postdonation ESRD risk in LKDs. Careful monitoring of early postdonation eGFR is essential to provide adequate postdonation care and counseling.
CITATION INFORMATION: Massie A., Fahmy L., Henderson M., Thomas A., Snyder J., Segev D. Pre-Donation eGFR, Early Post-Donation eGFR, and Subsequent ESRD Risk in Living Kidney Donors Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Massie A, Fahmy L, Henderson M, Thomas A, Snyder J, Segev D. Pre-Donation eGFR, Early Post-Donation eGFR, and Subsequent ESRD Risk in Living Kidney Donors [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pre-donation-egfr-early-post-donation-egfr-and-subsequent-esrd-risk-in-living-kidney-donors/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress