Phenotypic Classification of Acute Rejection Correlates with Long-Term Graft Survival
U of Cincinnati, Cincinnati
Christ Hospital, Cincinnati
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D1591
Effect of acute rejection (AR) type (antibody versus cellular versus mixed) and timing (early vs. late) on graft survival have not been concomitantly analyzed. This study evaluated graft and patient survival following first AR episode among kidney txp recipients with an early or late antibody-mediated (AMR), acute cellular (ACR), or mixed AR (MAR).
Methods: A prospective database was reviewed for biopsy-proven first AR episodes in 182 patients from 1/05 to 10/12. ACR was defined by Banff criteria; borderline rejections were excluded. AMR was defined as presence of 3 out of 4 criteria: renal dysfunction (increase in Scr by 0.3mg/dL or 15% from baseline), donor specific antibody, C4d positivity on biopsy, and/or glomerulitis or peritubular capillaritis. MAR episodes were defined as coexistence of ACR and AMR. Early and late rejections were defined as < or > 6 mos post-txp.
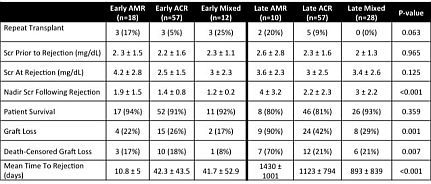
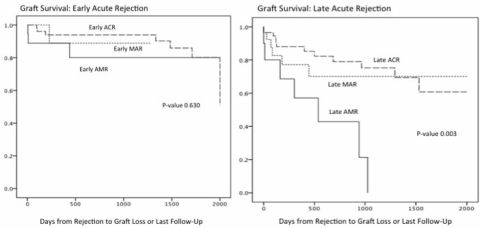
Results: Median follow-up post-rejection was 753 days (1-2573). No differences occurred between the 6 AR categories with respect to age, gender, African American ethnicity, repeat txp, or delayed graft function. Overall patient survival was 88% and death-censored graft survival was 79%. Graft loss was highest with late AMR and late ACR. Graft loss was greater with late vs. early AMR (p=0.01) but not late vs. early ACR (p=0.10) or late vs. early MAR (p=0.2).
Conclusion:
1. For all AR types graft loss was numerically worse with late rejection compared to early AR.
2. Rejection type demonstrated a hierarchy for graft survival with ACR>MAR>AMR.
3. The hierarchical relationships for graft survival (ACR>MAR>AMR) were similar between early and late AR.
4. Improvement in long-term results of AR therapy may require development of specific treatment for individual AR types.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Krisl J, Alloway R, Shields A, Govil A, Mogilishetty G, Cardi M, Diwan T, Jawdeh BAbu, Girnita A, Woodle E. Phenotypic Classification of Acute Rejection Correlates with Long-Term Graft Survival [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/phenotypic-classification-of-acute-rejection-correlates-with-long-term-graft-survival/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
