Patient Survival After Living Donor Kidney Donation
Medical Department, Division of Nephrology and Internal Intensive Care Medicine, Charité, Berlin, Germany
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 953
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Living donor, Mortality, Survival
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Living donor kidney transplantation [LDKT] is associated with best patient survival and life quality among kidney replacement therapies in case of chronic kidney disease. As risk factors for recipient [rcpt] survival are variable in previous studies, we investigated in our center.
*Methods: All LDKT rcpts transplanted from 01.01.1997 to 18.03.2020 were analyzed retrospectively. Based on the relationship to their donor rcpts were grouped into “related [R]” (first-degree relatives or grandparents), “far related [FR]” (other biological relationships) and “unrelated [UR]” (not related). Endpoint of this study was patient and graft loss [pg] survival analyzed by Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. Independent risk factors were estimated with Cox-regression.
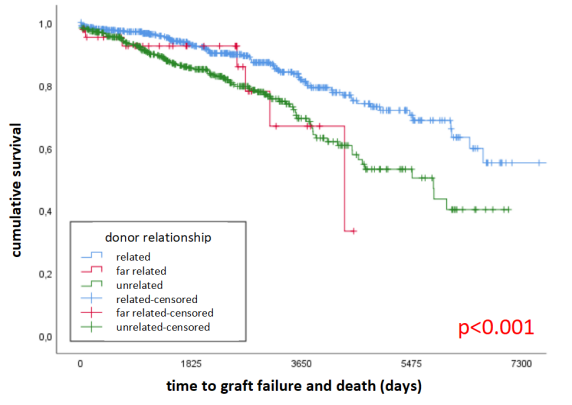
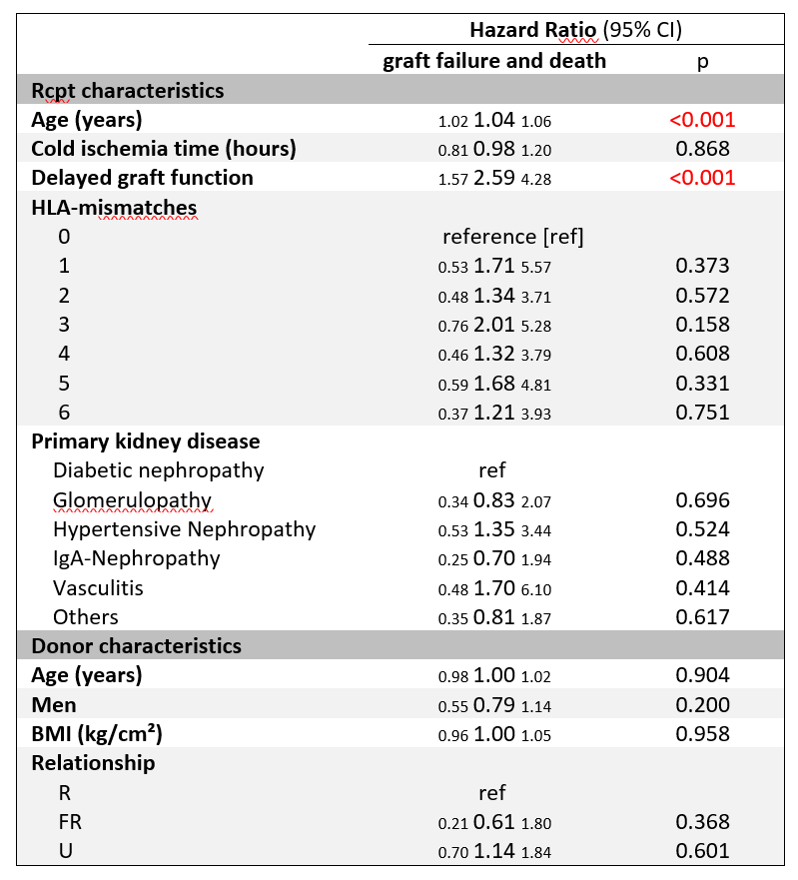
*Results: Among 946 LDKT rcpts we identified n=504 R, n=44 FR and n=398 UR rcpts. Overall 9.1% (86) grafts failed and 10.8% (102) died. Rates of graft failure and deaths were 8.7% and 6.7% in R rcpts; 9.1% and 11.4% in FR rcpts; 9.5% and 15.8% in UR rcpts. Kaplan-Meier-analysis (figure 1) showed overall pg survival of 89.8%, 76.3% and 48.3% with median follow-up time of 5.9 years. There was a significant difference in pg survival (p<0.001) between subgroups. In the multivariate analysis (figure 2) we observed delayed graft function (HR:2.59; p<0.001) and rcpt age in years (HR:1.04; p<0.001) as independent risk factors for pg survival.
*Conclusions: LDKT rcpt without biological relationship to their donors have inferior pg survival. The donor relationship as well as delayed graft function and rcpt age should be taken into account in patient evaluation. Rcpt with these characteristics should be informed about their individual risks and carefully monitored long term.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Naik MG, Sakurayama K, Budde K, Halleck F. Patient Survival After Living Donor Kidney Donation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/patient-survival-after-living-donor-kidney-donation/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress