Patient Reported Side Effects Associated with Reduced Quality of Life after Living Donor Kidney Transplant
Northwestern University, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B55
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Outcome, Quality of life
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: As living donor kidney transplant (LDKT) graft and patient survival approaches 100%, the focus of care turns to patient reported outcome measures such as health-related quality of life (HRQOL). We examined whether patient reported side effects from treatment was correlated with decreased HRQOL scores.
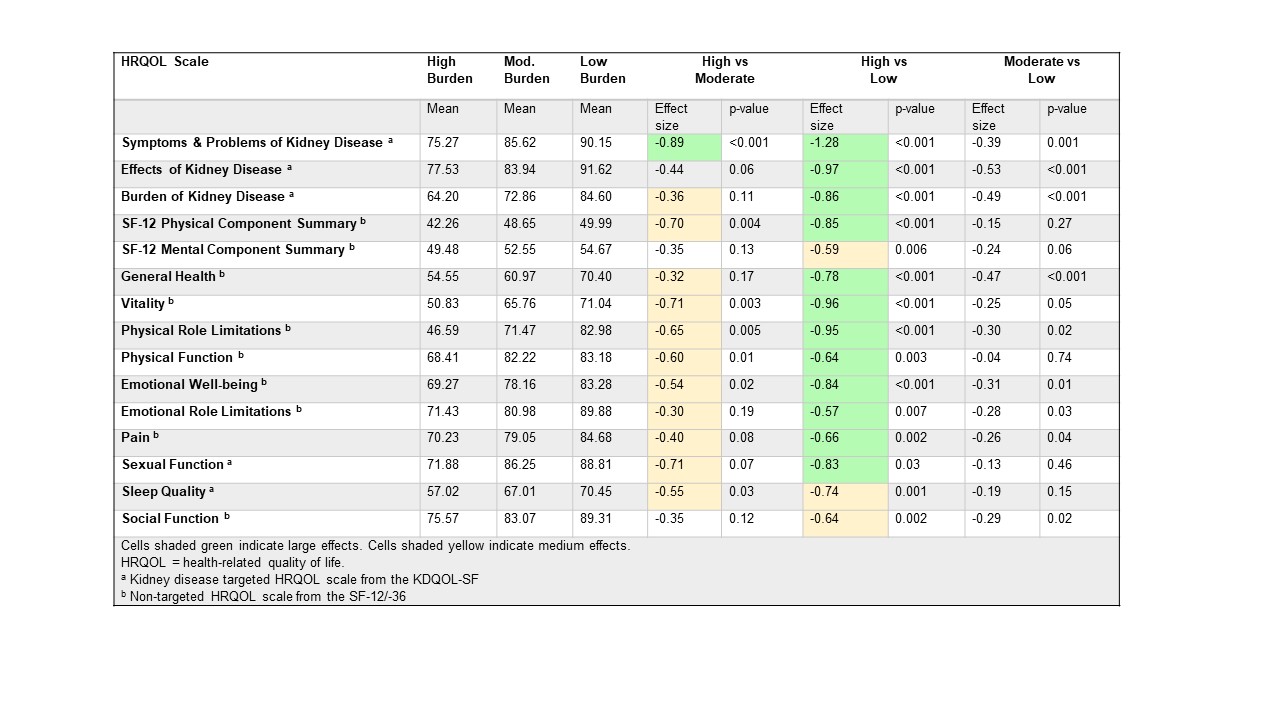
*Methods: We examined post-LDKT medication-related side effects among 404 patients transplanted between 11/2007 and 08/2016. We used a single question from the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Kidney Symptom Index (FKSI) to indicate medication side effect burden, “I am bothered by side effects of treatment” (GP5), at 3 and 12 months post-LDKT. We compared mean scores on 15 HRQOL scales from the Kidney Disease Quality of Life – Short Form (KDQOL-SF), which includes the SF-36, between patients reporting high side effect burden (defined as a response of “very much”/”quite a bit” on GP5), moderate side effect burden (defined as a response of “somewhat”/”a little bit”), and no side effect burden (”not at all”) using ANOVA. For each HRQOL scale, scores range between 0-100 and higher scores indicate better HRQOL. Standardized effect sizes were calculated and the following pre-specified cut-offs were used: 0.20 < d < 0.50 = small; 0.50 < d < 0.80 = medium; > 0.80 = large.
*Results: At both 3 and 12 months, a minority of patients (6-7%) reported high side effect burden, while 25-32% reported moderate burden. Mean differences between high vs. low side effect burden were of large magnitude (>0.80) for 8 scales and medium magnitude (>0.50) for 7 scales. (Table) Comparing high vs. moderate side effect burden, 1 scale had a large magnitude difference and 7 scales had a medium magnitude difference.
*Conclusions: More than a third of LDKT recipients were affected by medication side effect burden and this was associated with significant reductions in patient reported physical, mental/emotional, social, and functional HRQOL assessments. Optimizing post-LDKT immunosuppression regimens may increase LDKT’s benefits.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peipert J, Caicedo-Ramirez JC, Ensor K, Friedewald J, Abecassis M, Cella D, Ladner D, Butt Z. Patient Reported Side Effects Associated with Reduced Quality of Life after Living Donor Kidney Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/patient-reported-side-effects-associated-with-reduced-quality-of-life-after-living-donor-kidney-transplant/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress