Pancreas Transplant Alone Using Donation After Cardiac Death Donors Has Similar Outcomes As Donation After Brain Death Donors
1Washinton University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, 2Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO, 3Johns Hopkins University, St. Louis, MO
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 402
Keywords: Brain death, Donors, non-heart-beating, Pancreas transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics II
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Location: Room 209
*Purpose: While outcomes of pancreas transplants are improving, there is a persistent hesitancy to use pancreas organs procured in the context of donation after cardiac death (DCD) for pancreas transplant alone (PTA) because of concern of graft thrombosis and primary non-function organs. We report the outcomes of the first 43 DCD PTA in the United States.
*Methods: We examined Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) data for patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) who received PTA from donation after brain death (DBD, n= 1906) and DCD (n= 43) from January 2002 to December 2016. Associations of transplant type with all-cause graft failure and patient death (adjusted hazard ratio, 95% LCL aHR 95% UCL) were quantified by multivariate Cox regression including adjustment for recipient, donor, and transplant factors.
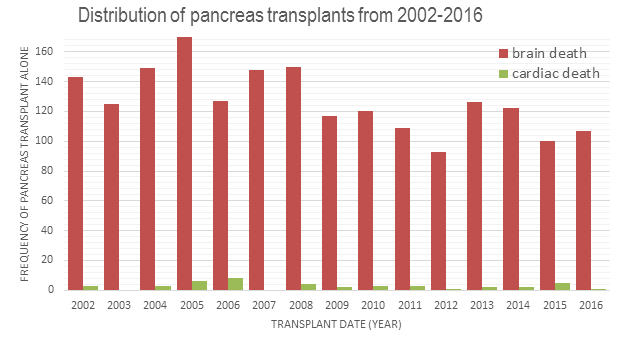
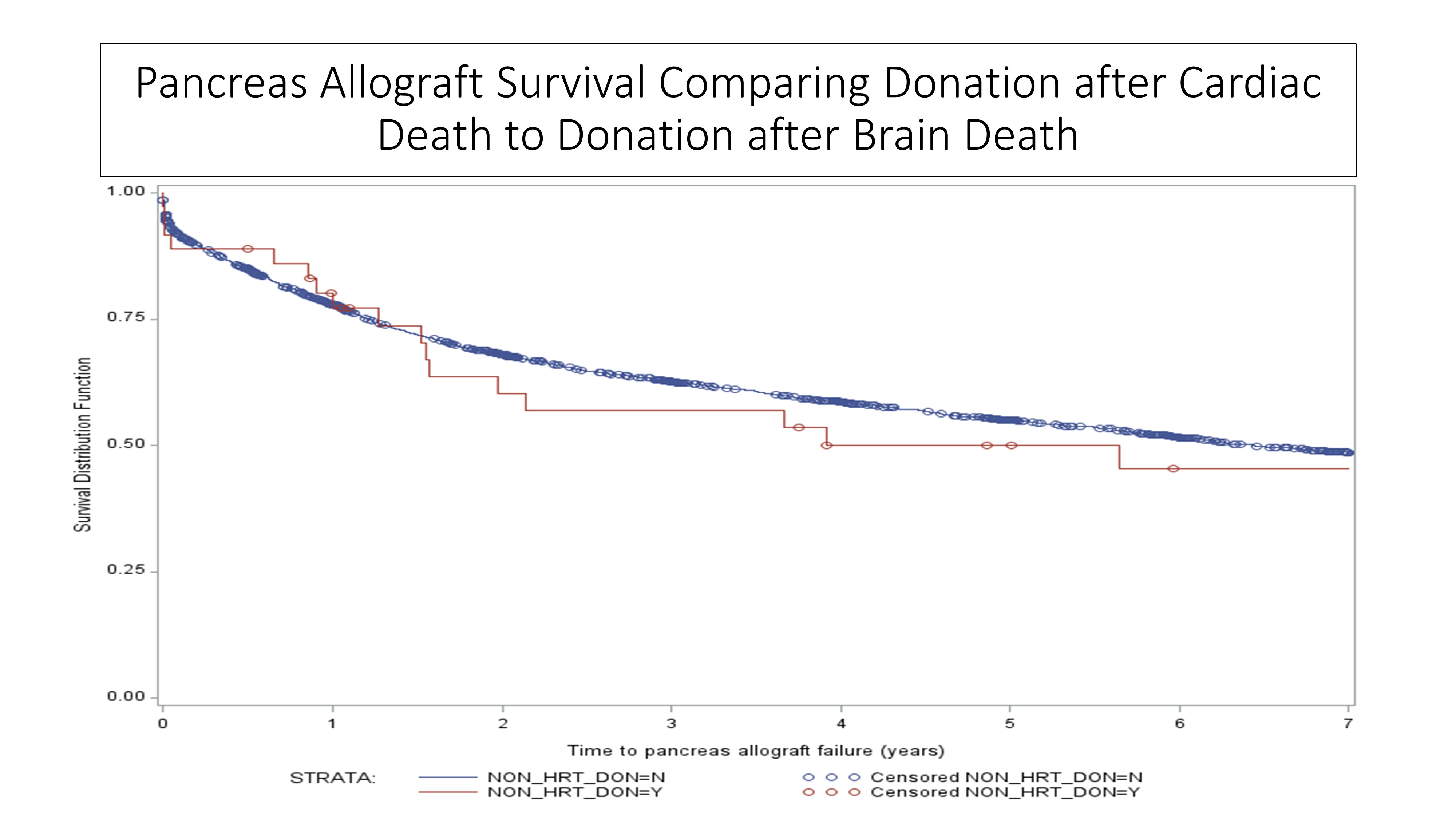
*Results: The average number of PTA declined from 145 per year in 2002-2008, to 112 per year in 2009-2016 (Figure 1). Region 7 performed the highest number of PTA (582 DBD, 26 DCD), followed by Regions 10 (413 DBD, 4 DCD), 2 (DBD 325, 2 DCD) and 3 (DBD 63, 0 DCD). Pancreas graft survival of DCD PTA was not significantly different than DBD at 1 year (75% vs 75%), 3 years (60 vs. 64%), and 5 years follow-up (50 vs 55%) (P=0.79) (Figure 2). Compared to DBD PTA, recipients of DCD PTA did not have a significant increase of risk of pancreas failure (aHR 0.751.221.99) or patient death (aHR 0.360.912.31).
*Conclusions: These data support that selected DCD PTA by experienced surgeons may be a successful option for pancreas transplantation, offering equivalent outcomes as pancreata procured after brain death.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Espinoza K, Wall D, Lentine KL, Wellen JR, Hammad D, Brennan DC, Alhamad T. Pancreas Transplant Alone Using Donation After Cardiac Death Donors Has Similar Outcomes As Donation After Brain Death Donors [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pancreas-transplant-alone-using-donation-after-cardiac-death-donors-has-similar-outcomes-as-donation-after-brain-death-donors/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress