Outcomes Of Treatment Of Late Vs Early Acute Antibody-mediated Rejection In Renal Transplant Recipients – A Single Center Experience
Henry Ford Transplant Institute, Detroit, MI
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D106
Keywords: Antibodies, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: The diagnostic accuracy and treatment options for acute antibody-mediated rejection (aABMR) in RTRs has improved over the last several years. However,response to treatment in early and late aABMR may differ. While successful reversal of early post-transplant aABMR is well documented, data on the results of treatment of late aABMR are lacking. We present a single center experience of outcomes of treatment in late vs early aABMR.
*Methods: All consecutive patients who received treatment for aABMR between January 2011 and December 2015 were retrospectively reviewed. RTRs were stratified as early aABMR (<6 months post-transplant) and late aABMR (>6 months post transplant). Graft and patient survival were compared between the two groups.
*Results: aABMR was diagnosed in 32 RTRs with a median follow-up of 24 months (range 2-67 months). 34%(11/32) had early and 66%(21/32) had late AMR. Demographic characteristics are described in
| Early ABMR | Late ABMR | |
| Age at transplant (years) mean +/- SD | 38.7+/-10.4 | 43+/-14 |
| Age at transplant (years) mean +/- SD | 72 | 61.9 |
| Living Donor (%) | 18.1 | 33.3 |
| DGF (%) | 36.3 | 1 |
| Race (AA)(%) | 63.6 | 50 |
| cPRA >30% (%) | 45.4 | 22 |
| Time to rejection (months) median | 1.5 | 35 |
and biopsy characteristics are described in
| Early ABMR | Late ABMR | |
| Mixed Rejection (%) | 36.3 | 62 |
| Chronic Rejection changes (%) | 0 | 38 |
| IFTA >25% (%) | 0 | 38 |
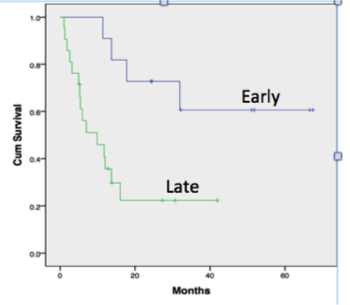
RTRs with late aABMR had significantly increased graft loss as compared to those with early aABMR (71.4% vs 36.3%) .
There was no statistically significant difference in patient survival between the two groups. However, 62%(13/21) of RTRs with late AMR had serious infections within 6 months of treatment.
*Conclusions: Our data suggest poor response to therapy in patients with late aABMR, with high risk of infectious complications. The risk of therapy of late AMR should be weighed against benefits, especially in patients with advanced renal failure and/or histological findings suggesting chronicity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Prashar R, Sulejmani N, Patel A. Outcomes Of Treatment Of Late Vs Early Acute Antibody-mediated Rejection In Renal Transplant Recipients – A Single Center Experience [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcomes-of-treatment-of-late-vs-early-acute-antibody-mediated-rejection-in-renal-transplant-recipients-a-single-center-experience/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress