Outcomes for Robotic Pancreas Transplants in Obese Candidates
University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 194
Keywords: Kidney/pancreas transplantation, Obesity, Outcome, Renal failure
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics I
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Room 209
*Purpose: Pancreas transplantation has evolved to include select overweight and obese diabetes mellitus (DM) patients. A robotic approach can be utilized to treat obese transplant candidates with the aim of reducing surgical complications and increasing access to pancreas transplantation.
*Methods: From October 2015 to July 2018, ten patients underwent robotic-assisted pancreas transplantation with eight being simultaneous kidney pancreas transplants. Intraoperative, patient and donor information were evaluated.
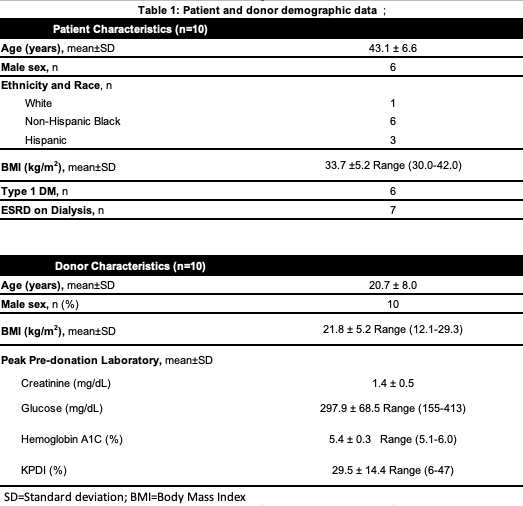
*Results: The average BMI of the recipients was 33.7±5.2 kg/m2 at the time of transplant. Patient and donor demographics are summarized in Table 1. Mean duration of operation for SPK was 8.3±0.8 hours while the median cold (CIT) and warm ischemia (WIT) times for the pancreas transplant were 8 (6.4-9.6) hours and 49 (42.8-55.3) minutes, respectively. Similarly, median CIT and WIT for the kidney transplants were 12 (10.8-12.3) hours and 45 (38-65.8) minutes. Seven patients were enterically drained. The median estimated blood loss was of 150 mL and median length of stay of 7 days. Median length of follow up is 15 (8-27) months with 5 patients having greater than a year of follow up. At 1 month follow up the average creatinine and glucose levels were 1.34±0.4mg/dL and 101±15.7, respectively, with all patient achieving sustained euglycemia with no insulin requirement. At time of last follow up, the average creatinine and glucose levels were 1.44±0.5mg/dL and 99±29.2, respectively.
*Conclusions: Robotic approach to pancreas transplantation in patients with elevated BMI appears to be safe and provides acceptable surgical outcomes and sustained graft function outcome.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Spaggiari M, Tulla KA, Okoye OT, Bella CDi, Cocco PDi, Alvarez JAAlmario, Tzvetanov IG, Benedetti E. Outcomes for Robotic Pancreas Transplants in Obese Candidates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcomes-for-robotic-pancreas-transplants-in-obese-candidates/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress