Outcomes Associated with Mycophenolate Weight-Based Dosing in Varying Immunologic Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients
Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, FL
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 327
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Mycophenolate mofetil, Risk factors, Weight
Session Information
Session Name: Immunosuppressive Drug Minimization
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Mycophenolate acid (MPA) is traditionally dosed in kidney transplant recipients (KTR) using the FDA-approved fixed dosing which is irrespective of patient-specific variables such as immunologic risk and actual body weight. This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of MPA weight-based dosing among low, moderate, and high immunologic risk KTR.
*Methods: In this retrospective, single-center study of adult (>18 years of age) KTR transplanted between 1/1/2015 and 12/31/2017, patients were stratified according to immunologic risk and MPA weight-based dosing. Standard-dosing was categorized as 20-33.9 mg/kg/day. The primary outcome was the incidence of biopsy-proven acute rejection (BPAR) at 1-year post-transplant between high immunologic risk KTR that received low doses of MPA compared to those that received standard and high doses. Secondary outcomes included eGFR at various time points, MPA-related readmission rates within 1-year, MPA-related adverse events leading to MPA dose reductions, BPAR at 1-year among low and moderate immunologic risk KTR, graft loss at 1-year, and all-cause mortality at 1-year.
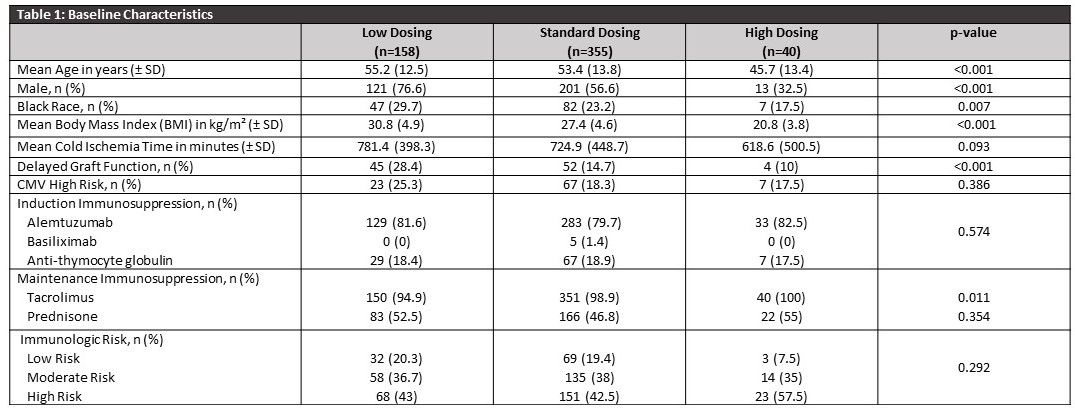
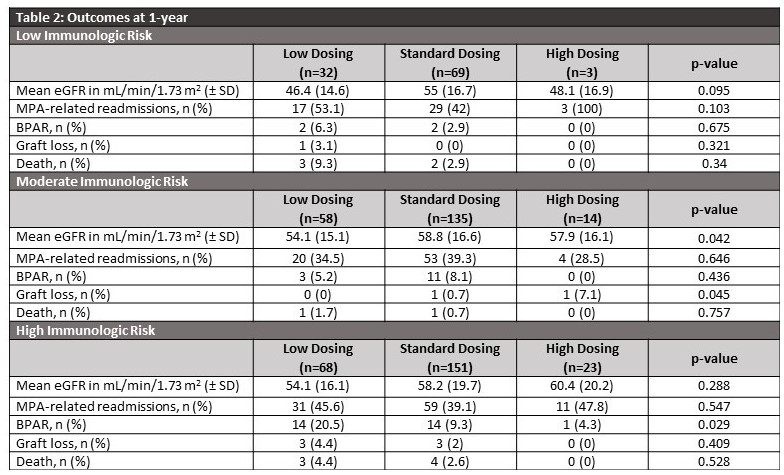
*Results: Of 648 KTR, 553 patients were included and categorized into low (n=158), standard (n=355), and high (n=40) dosing (Table 1). Patients who received lower doses had significantly higher BMIs compared to standard and higher dosing (p< 0.001). At 1-year post-transplant, the incidence of BPAR in high immunologic risk patients was 20.5%, 9.3%, and 4.3% in those who received low, standard, and high doses, respectively (p= 0.029). There were no statistically significant differences in MPA-related readmissions based on dosing within each immunologic risk group. The remaining results are presented in Table 2.
*Conclusions: Lower doses of MPA resulted in significantly higher rates of BPAR in high immunologic risk patients. These findings suggest that fixed doses of MPA without regard to actual body weight are not appropriate in high immunologic risk patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Al-Bahou AA, Webb AR, Bloxam M, Anger LJBowman, Baliga RS, Brueckner AJ. Outcomes Associated with Mycophenolate Weight-Based Dosing in Varying Immunologic Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcomes-associated-with-mycophenolate-weight-based-dosing-in-varying-immunologic-risk-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress