Optimizing Kidney Transplant Immunosuppression Using a Phenotypic Personalized Dosing Model
1Surgery, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, 2Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1704
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Infection, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 38 - Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
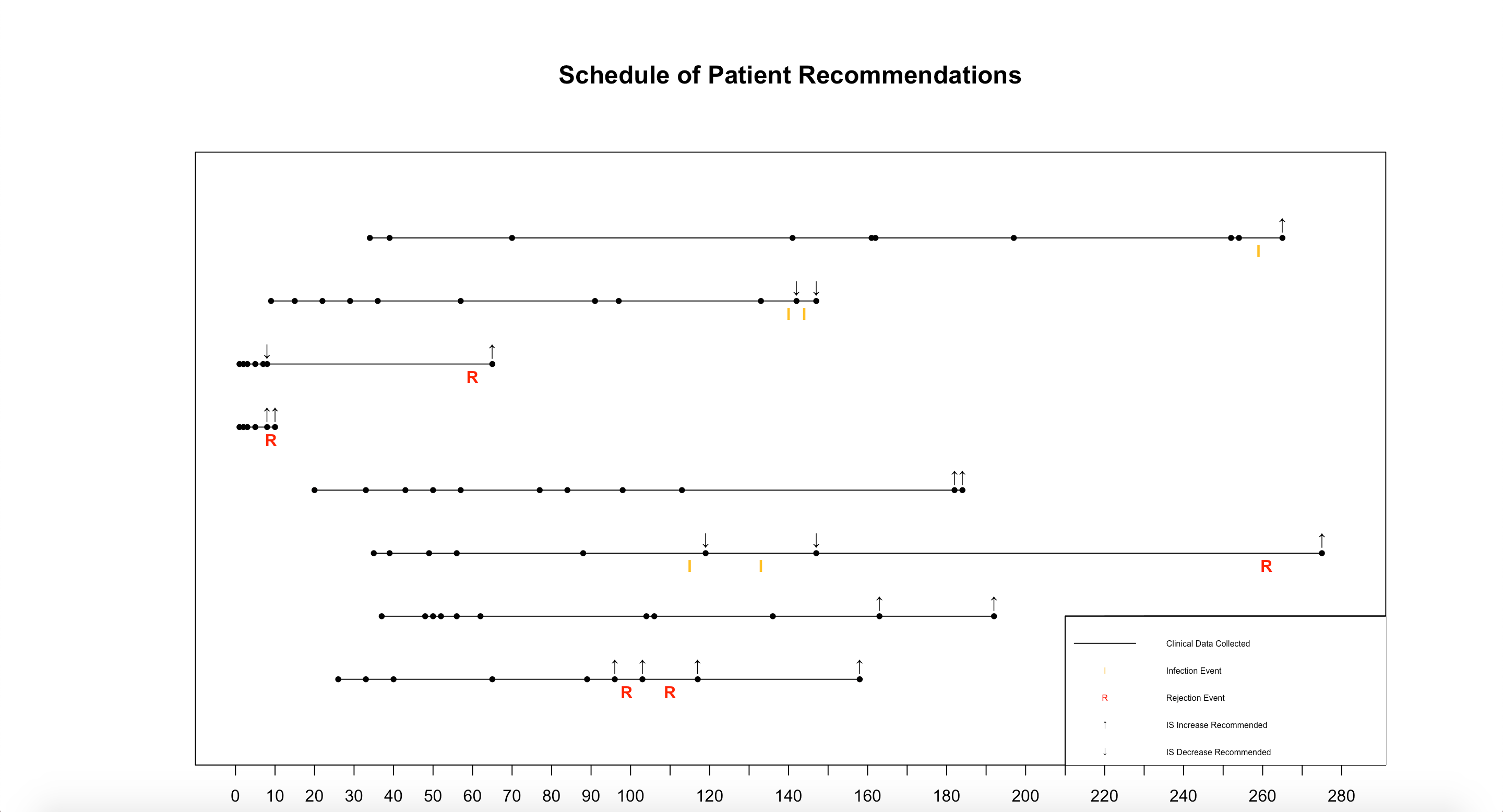
*Purpose: Immunosuppression is essential for preventing rejection and promoting long-term graft survival following solid organ transplantation; it also places patients at risk for infection and toxicity. Immunosuppression management is further complicated by individual variability in drug dosing, metabolism, and immune response. Hence adjusting immunosuppression continues to be a clinical challenge. We aimed to systematize multi-drug immunosuppression management in kidney transplantation using an artificial intelligence-based complex systems approach called phenotypic personalized medicine (PPM).
*Methods: PPM applies nonlinear regression to a patient’s clinical data to generate a mathematical representation of their response to immunosuppressive agents. This allows the identification of a combination of doses likely to produce a desired clinical outcome. For this project, our outcome was allograft status, informed by the donor-derived cell-free DNA fraction (dd-cfDNA).
Using PPM, we performed retrospective analysis on clinical data from 8 kidney transplant (KT) recipients to generate 17 IS dosing recommendations. Each recommendation is specific to both the patient and time of recommendation and is hence represented by a different equation with unique coefficients. As a result, we were able to sort recommendations by patient status at the time of the recommendation into stable (n = 7), infection (n = 6), or rejection (n = 5) groups.
We calculated recommended change in IS based on the difference between doses dictated by PPM and doses prescribed to patients. The strength of recommendations was quantified relative to the maximum for each immunosuppressive agent to reduce error caused by differences in scaling.
*Results: In a retrospective analysis of 8 kidney transplant patients, PPM successfully recommended increasing immunosuppression before and during patient rejection events. PPM also identified the need for decreased immunosuppression in patients who later developed infections. In cases of stable allograft status,PPM recommended a modest increase in immunosuppression.
*Conclusions: In this retrospective study of systematic AI-based individualized dosing, we have demonstrated a potential actionable strategy for multi-drug immunosuppression management.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bruner JF, Padmanabhan N, Ho C, Zarrinpar A. Optimizing Kidney Transplant Immunosuppression Using a Phenotypic Personalized Dosing Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/optimizing-kidney-transplant-immunosuppression-using-a-phenotypic-personalized-dosing-model/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress