Optimal Timing of Renal Transplantation in Simultaneous Heart-Kidney Transplant: A Retrospective Analysis of the UNOS/OPTN Database
Department of Surgery, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 34
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Multivariate analysis, Survival
Session Information
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: In patients receiving a simultaneous heart-kidney transplant (SHKT) the optimal timing of performing the kidney transplant remains controversial. In the immediate approach (iHKT), the kidney is transplanted during the same operative setting as the heart transplant. In the delayed approach (dHKT), the patient is taken to the intensive care unit to recover and after a period of stability, the kidney is transplanted in a separate operative setting. The purpose of this study was to determine whether the timing of the kidney transplant after heart transplant impacted long term patient and kidney graft survival in patients receiving SHKT.
*Methods: The UNOS STAR database was queried for all adult SHKT performed between 1998 and 2018. Patients who received SHKT were divided into two groups based on the timing of the kidney transplant. iHKT were defined as those with a differential cold ischemic time between the heart and kidney allografts (dCIT) of <6 hours and dHKT were defined as those with a dCIT of >6 hours. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed to determine patient survival and death-censored kidney graft survival (DSGS). Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression was used to adjust for donor and recipient factors.
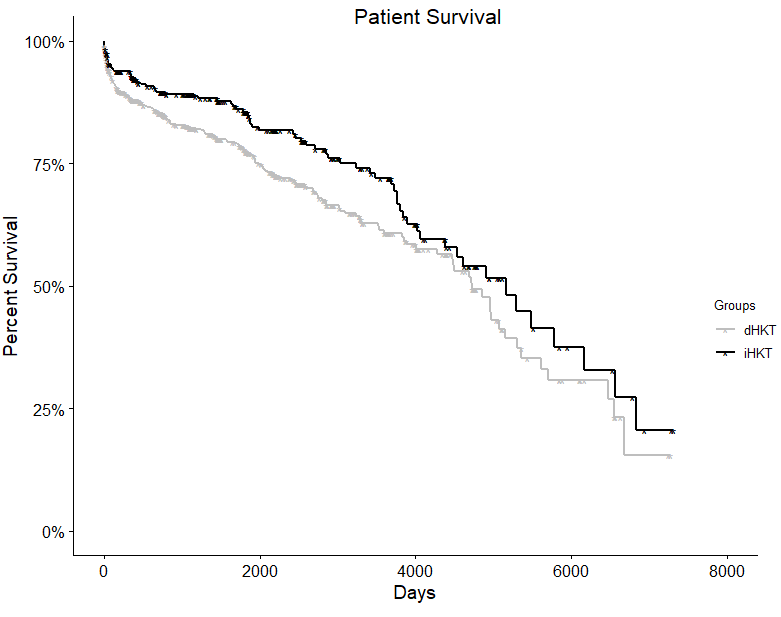
*Results: A total of 1170 SHKT recipients were identified. There were no differences in the iHKT and dHKT groups with regard to donor age, recipient age, body mass index, recipient gender, donor creatinine, donor hypertension, donor left ventricular ejection fraction, and KDPI. Donor vasopressin use was greater in the dHKT group (66% vs 59% in iHKT; p=0.015). Patient survival was significantly longer in iHKT vs. dHKT recipients at 1 and 3 years (1-year: 92.6% vs 88.0%, and 3-year: 89.3% vs. 82.3% in iHKT vs. dHKT respectively; adjusted p=0.006). DSGS was also greater in iHKT vs. dHKT at 1 and 3 years although not statistically significant (1-year: 98.0% vs 93.9%, and 3-year: 96.7% vs. 92.6% in iHKT vs. dHKT respectively; adjusted p=0.30).
*Conclusions: This study demonstrates that those patients undergoing iHKT have a significant survival benefit compared to patients undergoing dHKT. It is unclear whether kidney graft loss is impacting the patient survival benefit. Our study is limited in assessing the stability of the heart transplant recipient at the time of kidney transplant and this may have impacted the decision of timing for the kidney transplant. A carefully designed prospective study may be needed to better evaluate the effects of immediate versus delayed combined heart kidney transplants.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karim AS, Leverson GE, Smith JW, Foley DP. Optimal Timing of Renal Transplantation in Simultaneous Heart-Kidney Transplant: A Retrospective Analysis of the UNOS/OPTN Database [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/optimal-timing-of-renal-transplantation-in-simultaneous-heart-kidney-transplant-a-retrospective-analysis-of-the-unos-optn-database/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress