National Study of Living Donor Program Protocols, Processes, and Resources within U.S. Transplant Centers
1Vanderbilt University, Nashville
2Montana State University, Bonzeman
3Beth Israel Deaconess MC, Boston.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 530
Keywords: Donation, Kidney, Resource utilization
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Living Donation: Programmatic Issues
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Location: Room 6B
Purpose: There is limited research that describes living donor (LD) program processes and protocols. This study aimed to describe LD program protocols, processes, and resources within U.S. transplant centers.
Method: A survey was sent to the living donor coordinator (LDC) at every U.S. LD program (n=211; response rate=70%, total respondents=148). Descriptive statistics summarized survey responses.
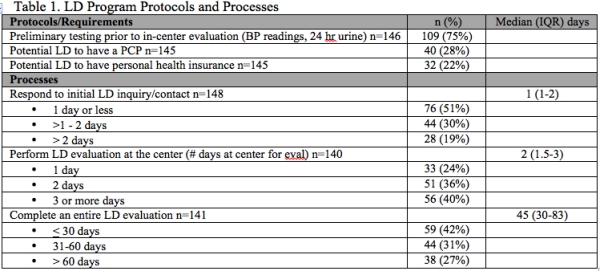
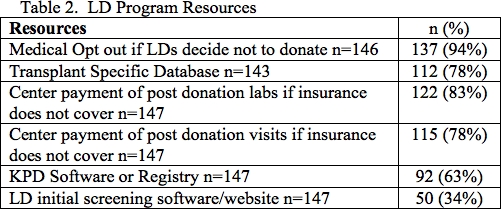
Results: 22% of centers required LD to have personal health insurance and 28% required LD to have a PCP (Table 1). Median time to respond to initial LD inquiry was 1 day (IQR 1-2) (Table 1). Median number of days LD required at the center for evaluation was 2 days (IQR 1.5-3) with 24% completing in center evaluation in 1 day and 40% of programs required > 3 days at the center. Median number of days to complete entire LD evaluation was 45 days (IQR 30-83) with 42% completing LD evaluation in < 30 days and 27% requiring > 60 days. 63% of centers had KPD software or registry. 83% of centers paid for the cost of post donation labs, 75% centers paid for post donation office visits, and 64% of centers covered the cost of post donation complications if insurance did not cover (Table 2). 94% offered the potential donor a medical opt out. 81% of centers accepted donors with controlled HTN. All centers reported a BMI restriction. 18% had BMI restriction < 30 and 61% had BMI restriction > 35. 43% reported upper age limits with 46% reporting upper age limit > 70 years.
Conclusions: Significant variability exists among centers in regards to program protocols and processes. This study is an important first step to identification of best practices among programs and program characteristics that are associated with higher numbers of living donor transplants.
CITATION INFORMATION: Moore D., Dietrich M., Buerhaus P., Rodrigue J., Minnick A. National Study of Living Donor Program Protocols, Processes, and Resources within U.S. Transplant Centers Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moore D, Dietrich M, Buerhaus P, Rodrigue J, Minnick A. National Study of Living Donor Program Protocols, Processes, and Resources within U.S. Transplant Centers [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/national-study-of-living-donor-program-protocols-processes-and-resources-within-u-s-transplant-centers/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress