Morbid Obesity and Functional Status as Predictors of Surgical Complication After Renal Transplantation.
Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 492
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Obesity, Risk factors, Surgical complications
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Diabetes and Obesity in Kidney Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Location: Room 302
Purpose: Surgical complications after renal transplant may impact patient morbidity and healthcare utilization. Identification of patients at risk would allow for planning allocation of resources and optimal management of these patients.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of adult patients who received kidney transplant from January 2010 through December 2014. Multi-organ transplants and patients with conversion to mTOR inhibitor within 30 days of transplant were excluded. Patients were first grouped by Kanorfsky functional status at baseline (low function ≤ 70%) and further stratified by presence of morbid obesity (BMI ≥ 35 mg/m2). Comparisons were made between BMI groups within each functional status category for the outcomes of surgical complications, delayed graft function (DGF), graft loss, and death.
Results: The analysis included 736 patients with similar baseline characteristics; differences were observed for history of diabetes and time of primary operation (Table 1). Surgical complications occurred in 184 (25%) patients, with no difference for low vs. high functional status or low vs. high BMI (Table 2). Among patients with low functional status, BMI ≥ 35 mg/m2 was associated with increased risk of surgical complication, superficial wound infection, and DGF compared with those without morbid obesity (Table 3, Figure 1). Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that morbid obesity and low functional status conditionally impact risk for surgical complications with an OR of 2.8 [95% CI (1.1, 7.3)] as compared with patients with high functional status and BMI < 35 mg/m2. There was not a significant difference in occurrence of graft loss or death across the cohorts (Figure 2). 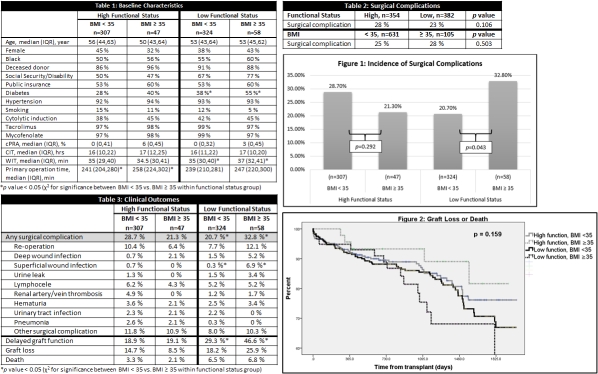
Conclusion: While neither morbid obesity nor poor functional status alone impacts outcomes, the combined presence is associated with significant increase in risk for surgical complications after renal transplantation. These patients may warrant more vigilance in the pre- and post-operative period to limit impact on patient morbidity and healthcare resources.
CITATION INFORMATION: Veasey T, Fleming J, Strout S, Miller R, Pilch N, Meadows H, Mardis C, Mardis B, Baliga P, McGillicuddy J, Taber D. Morbid Obesity and Functional Status as Predictors of Surgical Complication After Renal Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Veasey T, Fleming J, Strout S, Miller R, Pilch N, Meadows H, Mardis C, Mardis B, Baliga P, McGillicuddy J, Taber D. Morbid Obesity and Functional Status as Predictors of Surgical Complication After Renal Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/morbid-obesity-and-functional-status-as-predictors-of-surgical-complication-after-renal-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
