Low Kidney Supply to Demand Ratio and Multi-Organ Transplant Centers Are Negatively Associated with Pediatric Renal Transplant Rates Post Kidney Allocation System Implementation: An Analysis of OPTN Data
1CPSST Departments of Surgery and Renal Transplantation, Driscoll Children's Hospital, Corpus Christi, TX
2UNOS, Richmond, VA.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 234
Keywords: Allocation, Kidney, Pediatric
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Pediatrics - 2
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Location: Room 3AB
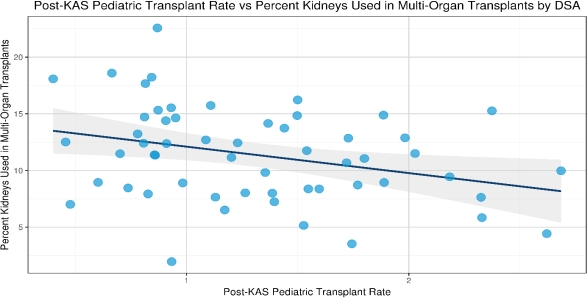
Under the new kidney allocation system (KAS), pediatric (PED) renal (REN) transplant (Tx) candidates have priority to kidneys from donors with KDPI < 35%. We hypothesized that PED REN Tx rates (TR) vary by donor service area (DSA) based on the presence of a multi-organ Tx center (MOTx) and supply to demand ratio (SDR) (# of KDPI<35% kidney donors recovered divided by PED candidates in the DSA. For MOTx we included kidneys recovered in the DSA but used either locally or non-locally. We analyzed UNOS data (Pre-KAS: 12/4/2012-12/3/2014 vs. post-KAS: 12/4/2014 to 12/3/2016). TR is the number of kidney alone Tx per active patient-year. Tx relative ratio (TRR) is post-KAS TR divided by pre-KAS TR. Although national PED REN TR remained unchanged; pre-KAS {(1.033) vs. post-KAS (1.030) (CI 0.916, 1.085)}, 4 DSAs had a significant increase, and 3 had a significant decrease in PED REN TRR. Similarly, 11 Tx centers had a significant increase, and 4 had a significant decrease in their PED REN TRR. However, the DSA and center level differences did not persist after correcting for multiple comparisons (Bonferroni method). Scatter plots showed a significant positive correlation between SDR and post-KAS PED REN TR [Figure 1], p=.02, and significant negative correlation between PED REN TR and MOTx [Figure 2], p=.01. This study shows several findings. First, the proportion of kidneys used for MOTx by DSA, was negatively associated with PED REN TRs. Second, PED REN TRs are lower for candidates listed in DSAs with fewer kidney donors with KDPI<35%. Additional KAS studies are needed to determine other factors that may contribute to inequities, limited access, and decreases in PED REN TR.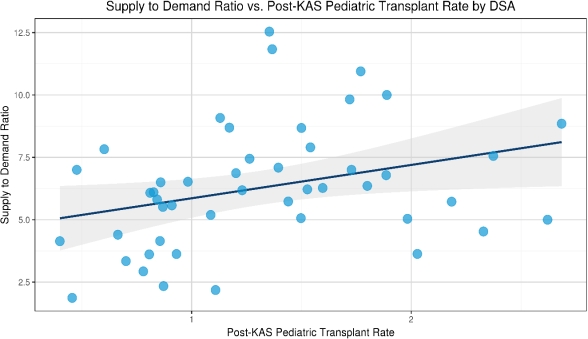
CITATION INFORMATION: Almond P., Al-Akash S., Stewart D., Robinson A. Low Kidney Supply to Demand Ratio and Multi-Organ Transplant Centers Are Negatively Associated with Pediatric Renal Transplant Rates Post Kidney Allocation System Implementation: An Analysis of OPTN Data Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Almond P, Al-Akash S, Stewart D, Robinson A. Low Kidney Supply to Demand Ratio and Multi-Organ Transplant Centers Are Negatively Associated with Pediatric Renal Transplant Rates Post Kidney Allocation System Implementation: An Analysis of OPTN Data [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/low-kidney-supply-to-demand-ratio-and-multi-organ-transplant-centers-are-negatively-associated-with-pediatric-renal-transplant-rates-post-kidney-allocation-system-implementation-an-analysis-of-optn-d/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
