Low Fixed Tacrolimus Starting Dose and the Correlation with Renal Allograft Rejection
David Geffen School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1677
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 34 - Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
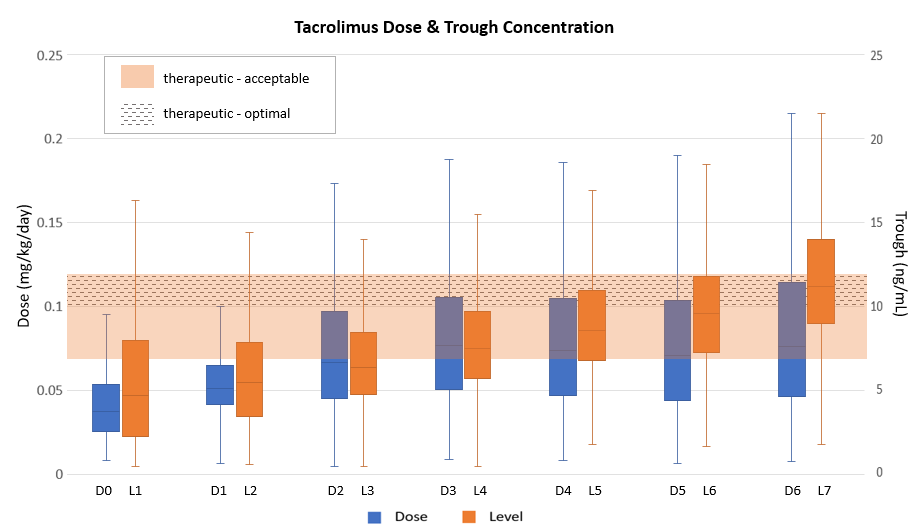
*Purpose: Achieving a tacrolimus therapeutic trough concentration (C0) by post-operative day (POD) 3-7 has been associated with a reduced risk for rejection. Although FDA prescribing information recommends a weight-based initial dose, the optimal starting dose of tacrolimus is unclear. We assessed if a fixed initial dose of tacrolimus 2 mg twice daily starting pre-operatively achieved target tacrolimus C0 by POD 3 or 7.
*Methods: We performed a single-center, retrospective review of adult primary renal transplants performed between 2017-2019. Patients received rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin or basiliximab induction and maintenance immunosuppression with tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and prednisone. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with a tacrolimus C0 of <7 ng/mL (subtherapeutic), 7-12 ng/mL (acceptable therapeutic), 10-12 ng/mL (optimal therapeutic), and >12 ng/mL (supratherapeutic) on POD 3 and 7. Secondary outcomes included the incidence of acute rejection at 1-year. Results are reported as descriptive statistics and evaluated with chi-square test.
*Results: 857 patients were included. On POD 3, 56.7%, 35%, 7%, and 8.3% of patients had subtherapeutic (Sub), acceptable therapeutic (AT), optimal therapeutic (OT), or supratherapeutic (Sup) tacrolimus C0, respectively. On POD 7, 8.5%, 50.6%, 23.5%, and 41% of patients had Sub, AT, OT, or Sup tacrolimus C0, respectively. Eighty-one (9.5%) patients had acute rejection with no difference in the incidence based on induction agent (p=0.167). Graft loss occurred in 8 (1%) patients with all-cause mortality in 12 (1.4%) patients. The 1 year acute rejection rate was 8.3%, 11.7%, 13.3%, and 8.1% on POD 3 and 4.2%, 11.8%, 14%, and 7.6% on POD 7 for patients who had Sub, AT, OT, or Sup tacrolimus C0, respectively. There was no increase in rejection rate in patients with subtherapeutic tacrolimus C0 at POD 3 or 7.
*Conclusions: By starting an initial fixed dose, 56.7% were subtherapeutic on POD 3 and 41% were supratherapeutic on POD 7 with dose titration. Yet, this did not correlate with increased rejection. Initiating tacrolimus at a higher dose, such as the FDA recommended dose, may help reduce the time to therapeutic tacrolimus C0.
| All Patients (N=857) | rATG (N=454) |
IL2RA (N=403) |
|
|
Acute rejection, n (%) |
81 (9.5) |
37 (8.1) |
44 (10.9) |
| Borderline |
25 (2.9) |
12 (2.6) |
13 (3.2) |
| Confirmed | 56 (6.5) | 25 (5.5) | 31 (7.7) |
| All-cause mortality, n (%) | 12 (1.4) | 5 (1.1) | 7 (1.7) |
| Graft loss, n (%) | 8 (1.0) | 4 (0.9) | 4 (1.0) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Davoudi R, Kitchel E, Lee S, Tan T, Sievers T, Bunnapradist S. Low Fixed Tacrolimus Starting Dose and the Correlation with Renal Allograft Rejection [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/low-fixed-tacrolimus-starting-dose-and-the-correlation-with-renal-allograft-rejection/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress