Liver Allograft Provides Protection Against Cardiac Allograft Rejection In Combined Heart And Liver Transplantation
1Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 2Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA, 3Pathology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 4Gastroenterology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 5Cardiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B114
Keywords: Liver grafts, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Heart and VADs: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Combined heart-liver transplant (CHLT) is indicated for patients with combination of heart and liver disease or amyloid heart disease for whom liver transplant can stop its progression. Limited data suggests that the liver allograft provides immuno-protection for heart and kidney allografts in the setting of combined transplantation from the same donor. We hypothesized that CHLT would reduce the incidence of acute cellular rejection (ACR) and development of donor specific antibodies (DSAs) compared with heart transplant alone (HA).
*Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of 33 CHLT compared to 283 HA recipients. The primary outcome was incidence of ACR per protocol and indicated myocardial biopsy. Rejection was graded according to International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) guidelines with Grade 2R and 3R considered significant. The secondary outcomes included development of new DSAs
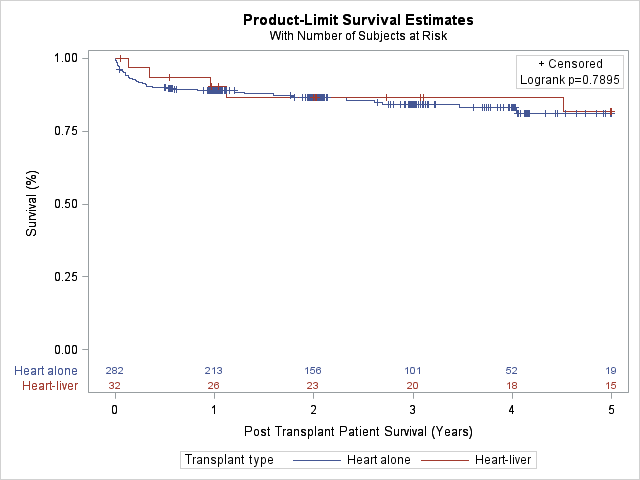
*Results: 9.1% of CHLT patients had ACR compared to 42.7% of HA (P = 0.0002). Pre-transplant cPRA levels were similar between groups (mean cPRA 9.4% vs. 9.3%). Among patients who underwent testing, 26.9% of the CHLT and 17.3% of HA developed DSA (P = 0.227). Despite the difference in ACR incidence, overall survival and cardiac graft survival were similar at 5 years (Overall: CHLT 81.8% vs. HA 81.2%, P = 0.79; Graft: CHLT 81.8% vs. HA 80.8%, P = 0.75).
*Conclusions: CHLT reduced the incidence of ACR in the cardiac allograft suggesting that liver offers immuno-protection against cellular mechanisms of rejection. However, CHLT did not reduce incidence of DSA development, portending similar long-term survival among cardiac allografts in CHLT and HA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhao K, Wang R, Kamoun M, Olthoff K, Hoteit M, Rame E, Levine M, Mclean R, Abt P. Liver Allograft Provides Protection Against Cardiac Allograft Rejection In Combined Heart And Liver Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/liver-allograft-provides-protection-against-cardiac-allograft-rejection-in-combined-heart-and-liver-transplantation/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress