Kidney Retransplantation Is Associated with Higher Mortality Risk Among HIV+ vs. HIV- Recipients.
1School of Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
2School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
3Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients, Minneapolis, MN
4School of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 69
Keywords: HIV virus, Kidney, Outcome, Retransplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: SOT: HIV, HBV, & HCV
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Location: Room 313
Background: Excellent outcomes have been demonstrated in HIV+ kidney transplant (KT) recipients, yet no study has explored outcomes among HIV+ reKT recipients.
Methods: 4,683 adult reKT recipients with known HIV status reported to SRTR (1988-2013). Survival analysis was conducted with date of reKT as the start date. Survival time was compared using Kaplan-Meier curves, and Cox proportional hazards models were used to examine patient survival. Models were adjusted for recipient age, race, HCV status, KDPI, donor type, and transplant year.
Results: HIV+ reKT recipients experienced a 2.7-fold increased risk of death compared to HIV- reKT recipients (aHR: 2.74, 95%CI: 1.68-4.47, p < 0.001). 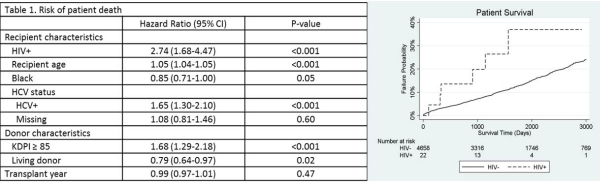 Traditional risk factors remained predictive, with high KDPI grafts conferring a 1.7-fold increased risk of death compared to grafts with a KDPI < 85 (aHR: 1.68, 95%CI: 1.29-2.18, p < 0.001) and 20% lower risk of death experienced by recipients of a living donor compared to recipients of a deceased donor. HCV infection was associated with a 1.7-fold higher risk of death compared to HCV- recipients (aHR: 1.65, 95% CI: 1.30-2.10, p < 0.001).
Traditional risk factors remained predictive, with high KDPI grafts conferring a 1.7-fold increased risk of death compared to grafts with a KDPI < 85 (aHR: 1.68, 95%CI: 1.29-2.18, p < 0.001) and 20% lower risk of death experienced by recipients of a living donor compared to recipients of a deceased donor. HCV infection was associated with a 1.7-fold higher risk of death compared to HCV- recipients (aHR: 1.65, 95% CI: 1.30-2.10, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: HIV-infected reKT recipients have increased risk of death compared to their HIV- reKT counterparts. Use of allografts with KDPI > 85% and recipient HCV coinfection are strong predictors of death among HIV+ reKT recipients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Shelton B, Mehta S, Sawinski D, Reed R, MacLennan P, Gustafson S, Durand C, Segev D, Locke J. Kidney Retransplantation Is Associated with Higher Mortality Risk Among HIV+ vs. HIV- Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shelton B, Mehta S, Sawinski D, Reed R, MacLennan P, Gustafson S, Durand C, Segev D, Locke J. Kidney Retransplantation Is Associated with Higher Mortality Risk Among HIV+ vs. HIV- Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kidney-retransplantation-is-associated-with-higher-mortality-risk-among-hiv-vs-hiv-recipients/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
