KDPI-Based Kidney Discard Risk Assessment
1IEMS Department, MEAS, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, 2IEMS Department, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, 3Department of Mathematics, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, CA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-020
Keywords: Donors, marginal, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Despite the vital need, 3,553 (19%) deceased-donor kidneys were discarded in 2018 in the current US allocation system. The discard rate has remained at 18%-20% over the last decade.
*Methods: The cohort consisted of adult deceased donor kidneys donated between 12/3/2014-03/01/2019. Two logistic regression models (KROD-A and KROD-B) using Kidney Donor Profile Index (KDPI) with additional covariates were fitted.
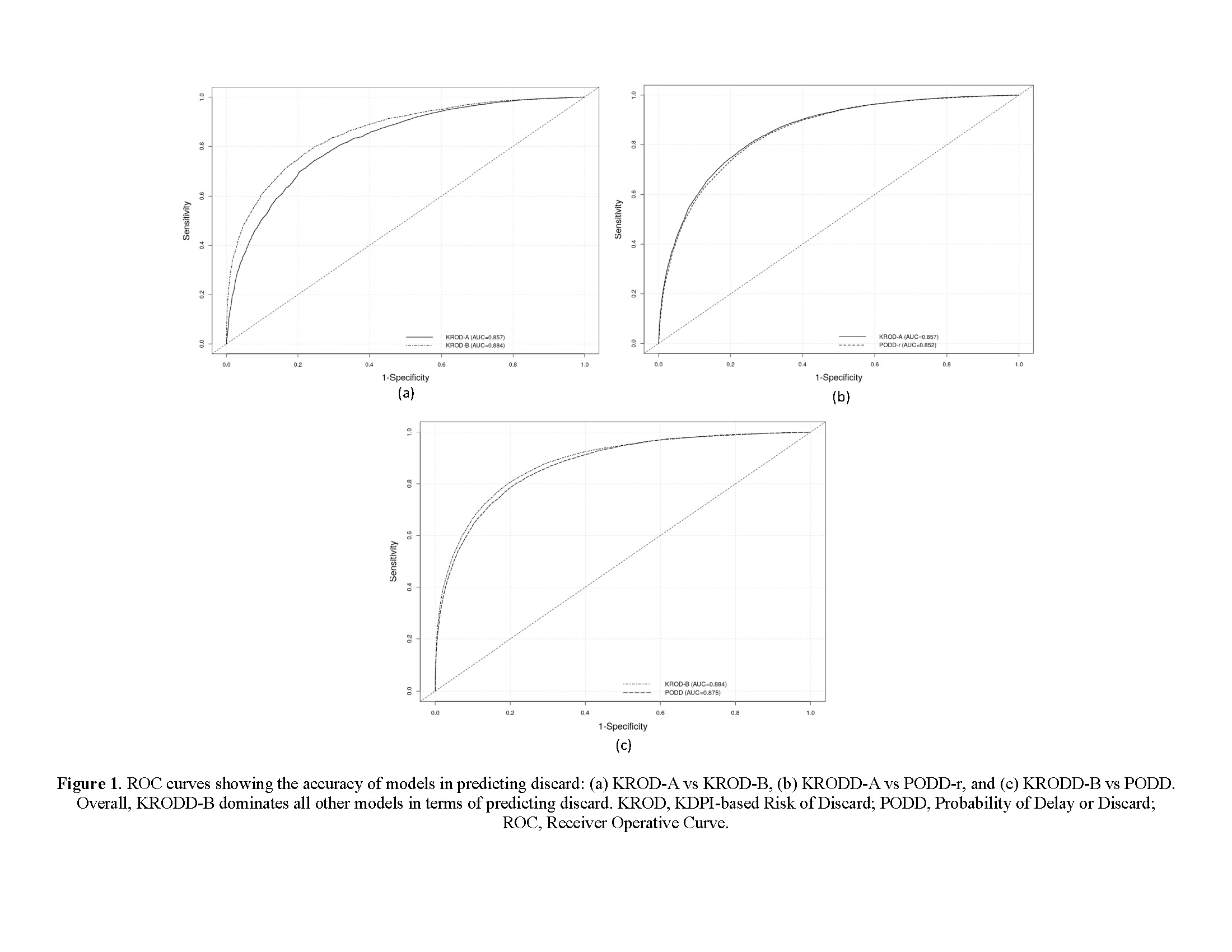
*Results: Kidney discards are predictable (KROD-A AUC=0.857, KROD-B AUC=0.884, Figure 1a). KDPI-based models improve over the probability of discard models (PODD-r AUC=0.853, PODD AUC=0.875, P<0.01, Figure 1b and 1c). A KDPI-only discard model’s AUC=0.773. The advantage of using KROD models is more pronounced when considering KDPI ≥ 75% kidneys discarded as “No recipient found, list exhausted” (KROD-B accuracy=79.97% vs PODD accuracy=69.58%). In the KROD-A model, the most notable predictors of discard are hepatitis C (OR=7.43), KDPI >95% (OR=5.78), hepatitis B surface antigen (OR=4.03), tumor (OR=3.94), and KDPI (90%, 95%] (OR=3.04), and. The OR is >1.5 for donors with KDPI (80, 85%] and (85%, 90%], terminal creatinine >1.5 mg/dL, DCD, diabetes >10 years, and positive hypertension. Glomerulosclerosis >20% (OR=16.03), (15%, 20%] (OR=4.59) are the notable predictors in KROD-B model along with the variables in KROD-A model. Secondary analysis shows that KDPI >75% kidneys when biopsied and those on pump have a reduced risk of discard.
*Conclusions: KDPI-based risk scores can be incorporated in policies intended to reduce kidney discard rates. Further investigation of variables with effect additive to KDPI on discard is desirable.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mehrotra S, Barah M, Bui K. KDPI-Based Kidney Discard Risk Assessment [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kdpi-based-kidney-discard-risk-assessment/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress