Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Renal Transplant Recipients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Analysis
W. Cheungpasitporn1, C. Thongprayoon2, P. Ungprasert3, K. Wijarnpreecha4, F. T. Chebib2, P. T. Kroner4
1Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS, 2Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Department of Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, 3Clinical Epidemiology Unit, Department of Research and Development, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, 4Department of Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C209
Keywords: Intracranial aneurysms, Kidney transplantation, Mortality, Polycystic kidney disease
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the hospitalization rate for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) among renal transplant patients with adult polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) and its outcomes, when compared to non-ADPKD renal transplant patients.
*Methods: The 2005-2014 National Inpatient Sample databases were used to identify all hospitalized kidney transplant patients with an associated diagnosis of ICH. The inpatient prevalence of ICH, in-hospital mortality, the use of aneurysm clipping, hospital length of stay, total hospitalization cost and charge in ADPKD patients were compared to non-ADPKD patients, adjusting for potential confounders.
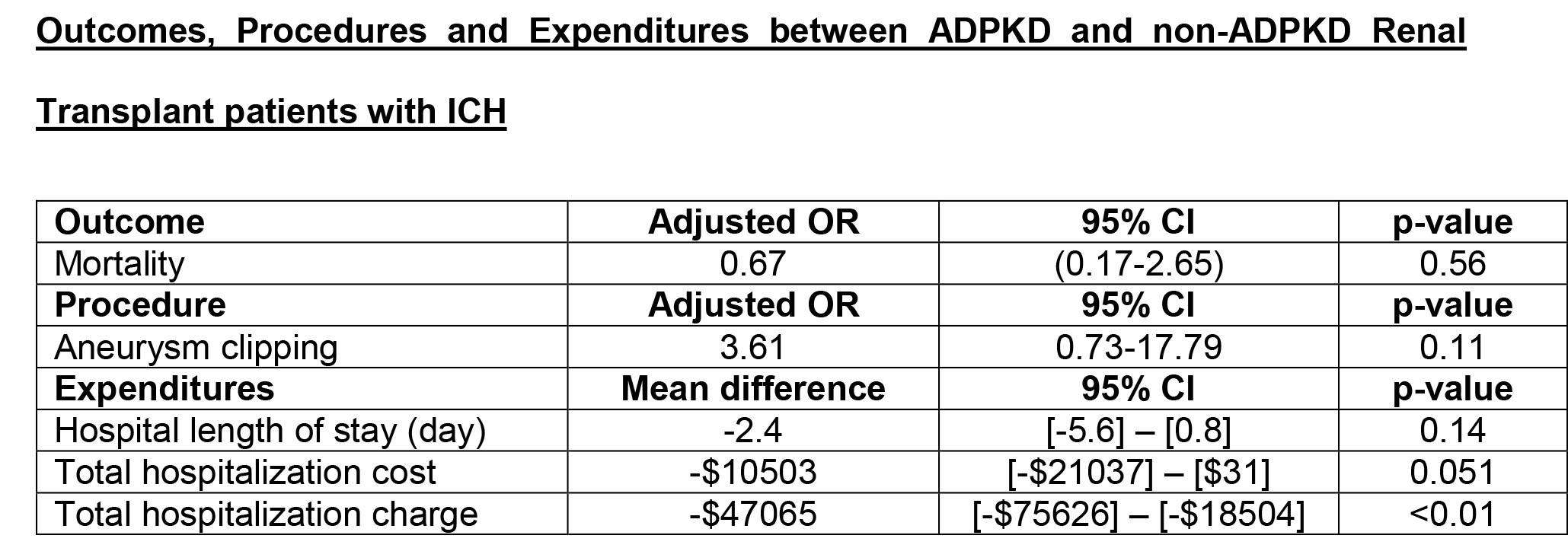
*Results: Of 4,239 renal transplant patients with an associated diagnosis of ICH, 76 had ADPKD. Inpatient prevalence of ICH in ADPKD was 9.5/1000 admissions, compared to 4.6/1000 admissions in non-ADPKD patients (p<0.01). A total of 15 (19.7%) ADPKD renal patients with ICH died in hospitals compared to 1,148 (27.6%) non-ADPKD renal patients (p=0.49). In adjusted analysis, there was no statistically significant difference in mortality, use of aneurysm clipping, hospital length of stay, and total hospitalization cost between ADPKD and non-ADPKD with ICH. However, total hospitalization charge was significantly lower in ADPKD patients than non-ADPKD patients.
*Conclusions: In this study using large U.S. Nationwide Inpatient Sample database, inpatient prevalence of ICH among ADPKD renal transplant patients was higher when compared with non-ADPKD renal transplant patients. In-hospital mortality of ICH among renal transplant patients was high, regardless of ADPKD status. While the uses of aneurysm clipping for ICH and hospital length of stay were comparable between ADPKD renal transplant patients and those without ADPKD, total hospitalization charge was lower in ADPKD renal transplant patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Ungprasert P, Wijarnpreecha K, Chebib FT, Kroner PT. Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Renal Transplant Recipients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Analysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/intracerebral-hemorrhage-in-renal-transplant-recipients-with-autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease-a-nationwide-analysis/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress