Intra-Graft Expression of Transcripts for Endothelial Activation and NK Cell Markers, Detected by Real-Time qPCR, Is Associated with the Presence of Donor Specific Antibodies, and Identifies Kidney Transplants at Risk of Failure
Imperial College Kidney &
Transplant Centre, Hammersmith Hospital, London, United Kingdom
Department of Medicine, Imperial College, London, United Kingdom
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 357
Background: Transcriptome analysis by micro-array from kidney transplant biopsy cores has identified genes associated with endothelial activation (ENDAT), and NK cell activity (NK), which are present in grafts undergoing antibody mediated rejection (AbMR). We have used a subset of the markers identified by Halloran, Sis, Mengel, Hidalgo et al to undertake analysis of biopsy-derived samples to specifically identify markers of AbMR by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Methods:Transplant biopsies taken for surveillance, or for cause, had one half core preserved for transcript analysis (but available for rescue to light microscopy). 36 biopsy samples taken for cause following the development of de novo donor specific antibodies, and 18 samples taken as 1-year surveillance biopsies during stable graft function were analyzed, using 5 ENDAT and 6 NK transcripts. Biopsies transcripts were scored as positive if they showed any transcript with Z-score >1.
Results: The presence of elevated ENDAT or NK transcripts was strongly associated with the finding of dsAbs (66% vs 33% Χ²p=0.02), but their presence in surveillance biopsies was not associated with subsequent immunological graft loss (100% survival with functioning graft at 2 years post-biopsy). Within the dsAb positive group, the detection of elevated ENDAT or NK transcripts was associated with immunological graft loss within 1 year from the date of the biopsy (graft survival 77% vs 92%).
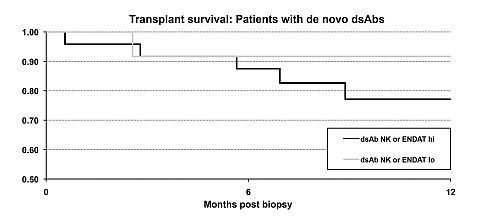
The presence of ENDAT or NK transcripts was correlated with the degree of microcirculatory injury (peri-tubular capillaritis or glomerulitis) on light microscopy.
Conclusions: qPCR analysis for ENDAT and NK transcripts of biopsy samples provides a rapid method for identifying grafts at risk of immunological graft loss. These data provide a validation set for the results from micro-array analysis.
McLean, A.: Grant/Research Support, Astellas Pharma.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McLean A, Dominy K, Kort HDe, Brookes P, Behmoaras J, Galliford J, Roufosse C, Cook T, Willicombe M, Taube D. Intra-Graft Expression of Transcripts for Endothelial Activation and NK Cell Markers, Detected by Real-Time qPCR, Is Associated with the Presence of Donor Specific Antibodies, and Identifies Kidney Transplants at Risk of Failure [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/intra-graft-expression-of-transcripts-for-endothelial-activation-and-nk-cell-markers-detected-by-real-time-qpcr-is-associated-with-the-presence-of-donor-specific-antibodies-and-identifies-kidney-tr/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
