Interactions of B and T Regulatory Cells in Normal Volunteers and in Tolerant HLA-Identical Kidney Transplant Recipients
Surgery
Comprehensive Transplant Center, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 239
Purpose: In an HLA Identical (id) renal transplant (RT) tolerance trial using donor hematopoietic stem cells, alemtuzumab induction, and temporary maintenance immunosuppression (IS), primarily with sirolimus, 5 of the first 10 recipients achieved non-chimeric tolerance (being IS-free for over 1 year with normal transplant biopsies). The present study was undertaken to assess the phenotypic and functional T and B immunoregulatory cells (regs) present in these tolerant recipients and to compare them with T and B regs generated in vitro in MLRs of normal volunteers.
Methods: We have tested the generation of functional Bregs (CD19+IL10+) and Tregs (CD4+CD25highCD127– FOXP3+) interactively in MLR assays both in normal volunteers and in HLA-id tolerant recipients.
Results: Immunoselected CD4+CD25+ Tregs generated in 7-day MLRs of normal laboratory volunteers when added as third component modulators inhibited proliferation of fresh MLR readouts from the same pairs and caused the generation of new Bregs by 5-10 fold in the responder cells. This was in contrast to PBMC modulator controls (n=9). These Bregs in turn could secondarily generate additional Bregs and Tregs (Fig. 1). We had previously published that such MLR induced Tregs similarly generated additional Tregs. HLA-id RT tolerant recipients developed significantly higher percentages of Tregs and naÏve B cells (the latter also contained putative Bregs) during the post-transplant period. When unselected post-transplant PBMC (>18 months) (vs. pre-transplant PBMC) were added into recipient’s donor specific MLR, there was an augmentation of newly generated Bregs and Tregs (n=4).
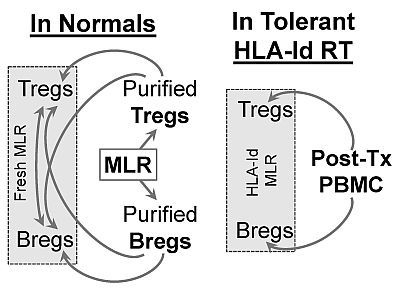
Summary and Conclusion: PBMC of post-transplant tolerant non-chimeric HLA-id recipients induced long-lasting functional Tregs and Bregs. These T and B regs were similar to those that could be generated in MLRs after immunoselection in normal volunteers. Such functional assays could possibly be used to discriminate between tolerant and non-tolerant transplant recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mathew J, Leventhal J, Huang X, Chen L, Tambur A, Friedewald J, Abecassis M, Miller J. Interactions of B and T Regulatory Cells in Normal Volunteers and in Tolerant HLA-Identical Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/interactions-of-b-and-t-regulatory-cells-in-normal-volunteers-and-in-tolerant-hla-identical-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
