Implementation of the Lung Allocation Score is Associated with Decreased Mortality in Combined Liver-Lung Allograft Recipients
1School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, NC
2Surgery, Duke University, Durham, NC.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C264
Keywords: Allocation, Mortality, Multivisceral transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Lung: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Objective: The current system for simultaneous liver-lung transplant (LLT) generally matches a recipient with a donor based on his or her lung allocation score (LAS), which results in a relatively low MELD score at transplantation compared to liver alone. However, the impact of LAS on LLT is unknown. To determine whether the current lung allocation system has improved survival in this cohort, we studied LLT before and after the introduction of LAS.
Methods: The OPTN/UNOS STAR file was queried for adult recipients of simultaneous LLT. Demographic characteristics were subsequently generated and examined. Kaplan-Meier with log-rank test compared survival between groups. A hazard ratio was generated based on the presence of LAS alone.
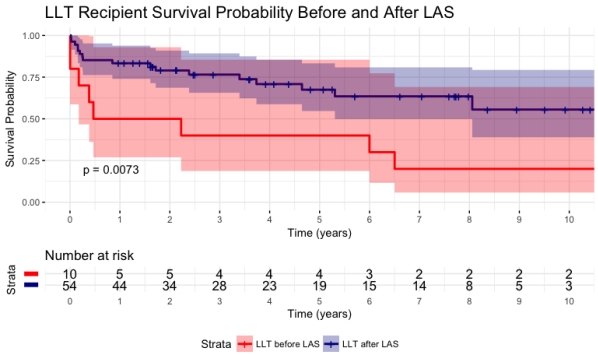
Results: A total of 64 LLT recipients were identified. Of which, 10 (15.6%) underwent transplant prior to the introduction of LAS. Comparatively, those without a LAS score had a higher FEV1 (48.22 vs. 29.56, p=0.012), higher creatinine at transplant (1.22 vs. 0.73, p=0.001), higher percent primary pulmonary hypertension (40% vs. 0%, p=0.004), and an earlier year of transplant (1999.4 vs. 2011.17, p<0.001). Length of stay, functional status, and acute rejection rate were not significantly different. Patient survival was significantly lower in the LLT cohort before the introduction of LAS compared to the cohort after LAS (Figure 1; 1-year: 50.0% vs. 83.3%, 5-year: 40.0% vs. 67.5%, 10-year: 20.0% vs. 55.6%, p=0.0073). Presence of LAS was associated with a lower risk of mortality (HR 0.33, 95% CIl 0.15-0.77, p=0.01).
Conclusions: LLT is a rare procedure and most national and center-level analyses have included patients before and after the introduction of the LAS. Our study shows that survival in LLT after the introduction of the LAS was significantly increased. While many factors contributed to the changes in mortality, the cohorts before and after the introduction of LAS are significantly different and should be treated as such when conducting future studies.
Figure 1: Ten-year Kaplan-Meier Overall Survival
CITATION INFORMATION: Freischlag K., Shroder P., Ezekian B., Mulvihill M., Knechtle S. Implementation of the Lung Allocation Score is Associated with Decreased Mortality in Combined Liver-Lung Allograft Recipients Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Freischlag K, Shroder P, Ezekian B, Mulvihill M, Knechtle S. Implementation of the Lung Allocation Score is Associated with Decreased Mortality in Combined Liver-Lung Allograft Recipients [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/implementation-of-the-lung-allocation-score-is-associated-with-decreased-mortality-in-combined-liver-lung-allograft-recipients/. Accessed March 8, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress