Impact of the Second Year COVID-19 Pandemic on the U.S. Kidney Transplantation: Interrupted Time Series Analysis
1Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Kidney Transplantation, Department of Medicine, University of California Irvine School of Medicine, Orange, CA, 2Faculty of Medicine Songklanagarin Hospital, Prince of Songkla University, Songkhla, Thailand, 3Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, 4Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1752
Keywords: COVID-19, Kidney, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 50 - Health Equity and Access
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The number of kidney transplant (KT) was decreased since the COVID-19 pandemic; however, the magnitude of the pandemic on the number of U.S. KT is unclear. We aim to examine KT access in the United States over the past 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
*Methods: The number of U.S. kidney transplant recipients from 1988 to 11/28/21 among 48 States performing KT and confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths were retrieved from OPTN/SRTR and CDC, respectively. The association of COVID-19 cases and deaths in 2020 and 2021 with the change in the number of KT were examined by linear regression. Interrupted time series defining the beginning of the pandemic in late 2019 as the time reflecting event change and Poisson regression were used to test the magnitude of KT decline since the beginning of pandemic.
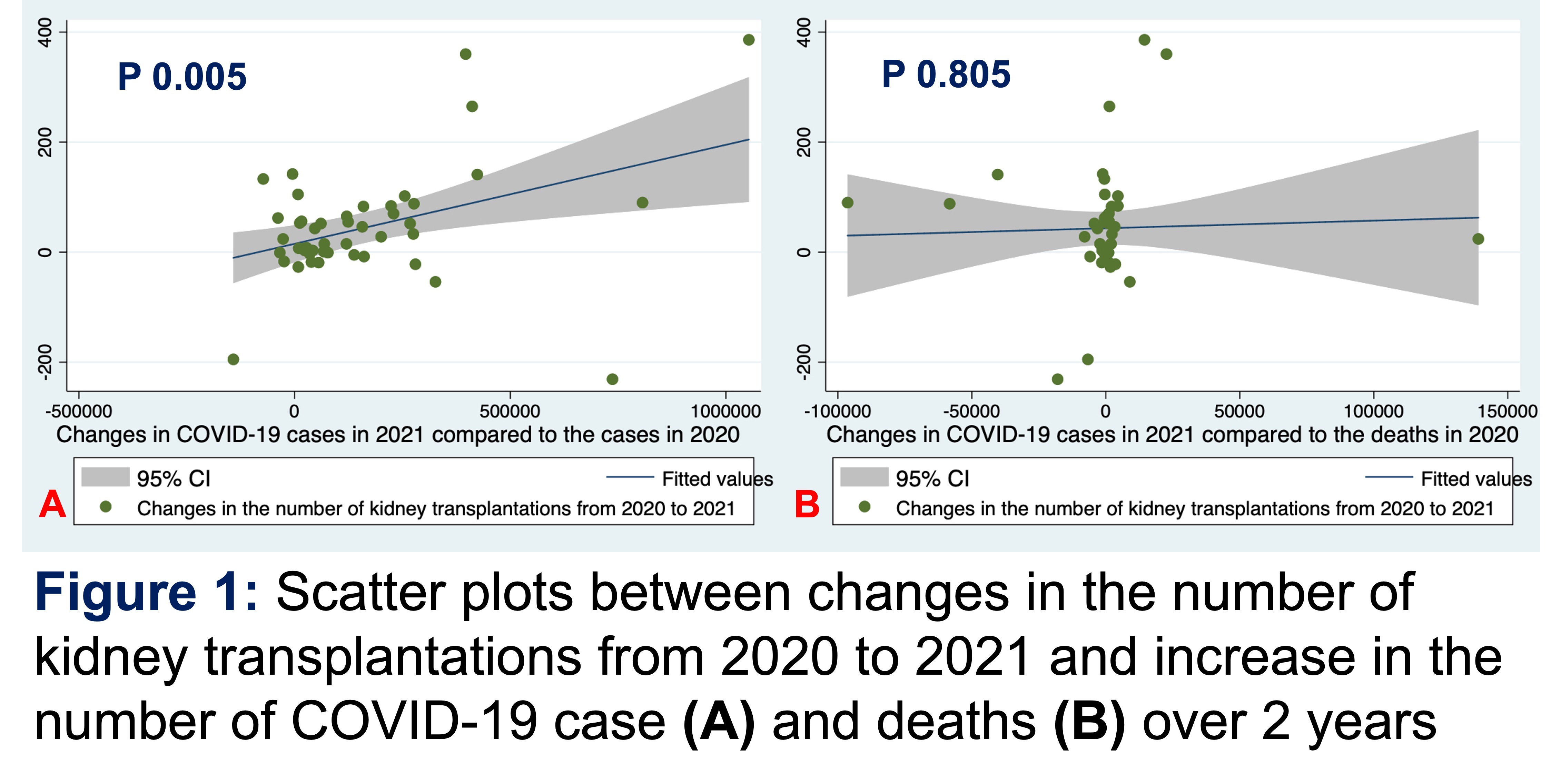
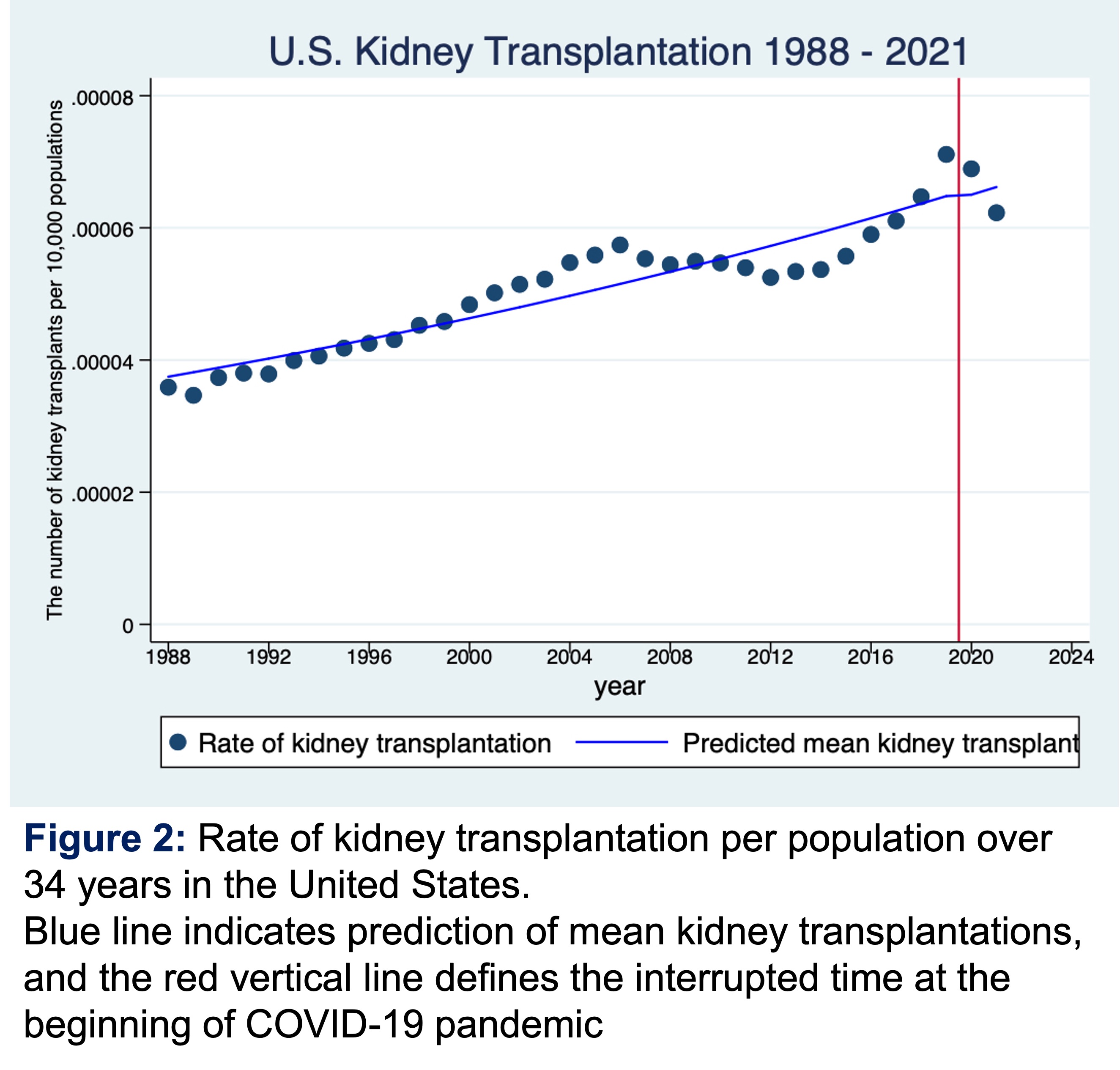
*Results: The number of KT had generally trended up from 1988 until 2019 when it has trended down (23,401, 22,817, and 20,736 in 2019, 2020, and 2021, respectively). The number of COVID-19 cases increased from 19,759,635 in 2020 to 27,284,847 in 2021 and mean COVID-19 death rate increased (227 and 340 deaths/10,000 COVID-19 cases; p 0.592). Compared to 2020, every 10,000 increased in COVID-19 cases in 2021 was associated with significant decrease in 18 KT; however, there was no significant association between the changes in COVID-19 deaths and KT between 2020 and 2021 (βcases 0.00018, p 0.005, 95%CI 0.00006, 0.00030 (Figure 1A) and βdeaths 0.00014, p 0.805, 95%CI -0.00098, 0.00126 (Figure 1B)). The number of KT after the COVID-19 pandemic is 1.43% lower than those before the pandemic (IRR 0.985, p 0.010, 95%CI 0.975, 0.997; Figure 2).
*Conclusions: Although ongoing COVID-19 pandemic over the past 2 years leads to increasing number of COVID-19 cases and deaths, only the number of COVID-19 cases, but not deaths, has significantly affected the number of KT in the United States.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tantisattamo E, Polpichai N, Mutirangura P, Tanariyakul M. Impact of the Second Year COVID-19 Pandemic on the U.S. Kidney Transplantation: Interrupted Time Series Analysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-the-second-year-covid-19-pandemic-on-the-u-s-kidney-transplantation-interrupted-time-series-analysis/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress