Impact of Renal Replacement Therapy Following Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation, The
Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Transplant Surgery, Mie Univeristy, Tsu, Japan
Cardiology and Nephrology, Mie Univeristy, Tsu, Japan
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D1691
Background: In deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT) settings, the post-transplant acute renal failure with the induction of renal replacement therapy (RRT) had negative effects on graft and patient survival after liver transplantation. However, the impact of RRT in living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) has not been well investigated.
Methods: Clinical data on the consecutive 111 adult patients who underwent LDLT at Mie University Hospital between March 2002 and October 2012 were retrospectively reviewed in this study. They were divided into the two groups: RRT (n=31) and No-RRT groups (n=80). The primary reasons for receiving RRT were hepatorenal syndrome (n=16), sepsis (n=12), and renal hypoperfusion (n=3).
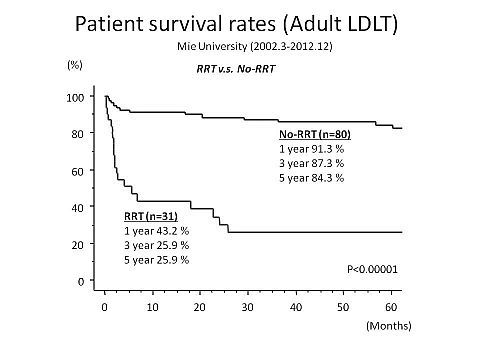
Results: Although there were no significant differences in age and gender, the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score was higher in RRT group than in No-RRT group (22 ± 12 vs. 16 ± 7, p =0.002). The graft recipient weight ratio (GRWR) was significantly lower in RRT group (0.86 ± 0.2 vs. 0.98 ± 0.2, p =0.022). The one- and five-yr patient survival rates were significantly higher in No-RRT group than in RRT group (91.3% and 84.3% vs. 43.2% and 25.9%, respectively, p < 0.001).
In multivariate analysis, independent risk factors for receiving RRT were MELD score (p=0.043) and GRWR (p=0.038). In RRT group, donor age (n=0.042) and preoperative serum creatinine level (n=0.049) were significant prognostic risk factors.
Conclusions: In adult LDLT patients, the induction of RRT after LDLT was a negative predictor of survival because RRT was not effective to control co-morbidities, particularly sepsis. In addition to the preoperative patient’s condition, donor factors including graft size and donor age influenced on postoperative acute renal failure with the induction of RRT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Iwata H, Mizuno S, Ishikawa E, Tanemura A, Kuriyama N, Ohsawa I, Azumi Y, Kishiwada M, Usui M, Sakurai H, Tabata M, Ito M, Isaji S. Impact of Renal Replacement Therapy Following Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation, The [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-renal-replacement-therapy-following-adult-living-donor-liver-transplantation-the/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
