Impact of Pre-Transplant Donor Renal Function on Graft Survival Following Kidney Transplantation
CTI Clinical Trial and Consulting Svcs, Raleigh
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Plainsboro
Duke University, Durham
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C1335
Introduction: Improved post-transplant renal function (RF) at 6 months is associated with improved long-term graft survival (GS). We evaluated how much of the impact of the reduction in early post-transplant RF on GS is due to pre-transplant donor RF.
Methods: RF was estimated by GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) in adult Medicare beneficiaries registered in the USRDS who received a kidney-only transplant from 2001-2008 using the MDRD equation, and categorized in the recipient by CKD stage defined by the National Kidney Foundation. Pre-transplant donor eGFR was calculated using the donor terminal serum creatinine. GS was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Impact of an unfavorable shift in CKD stage on the risk of graft failure (GF) was assessed by Cox hazards model using two models: one with and one without pre-transplant donor eGFR.
Results: A total of 76,514 patients were alive with a functioning graft and had eGFR data both pre-transplant and at discharge (mean age 50 years, 61% male, 29% Black, median follow-up of 4 years). Mean pre-transplant donor eGFR was 90.8. At discharge, 5% (n=3,496), 18% (n=13,816), 38% (n=29,310), 18% (n=14,131), and 21% (n=15,761) of patients were in CKD stage 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively. Patients in CKD stage 2, 3, or 4 at discharge who had a one stage worsening in CKD stage by month 6 had a significantly greater risk of graft failure at 4 years post-transplant (Table) adjusted for deceased vs. living donor.
Hazards ratios (HRs) with and without adjustment for pre-transplant eGFR were nearly identical.
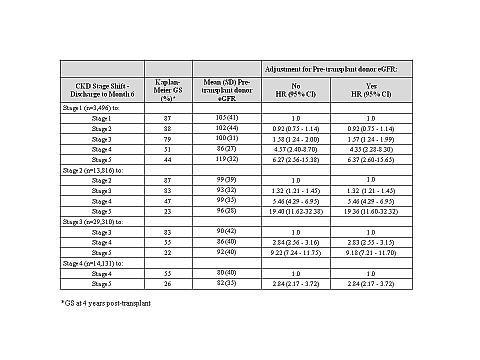
Conclusion: Pre-transplant terminal donor eGFR did not impact post-transplant GS. Loss of RF as measured by a one stage or greater reduction in CKD stage is most predictive of GF. Patient management strategies focused on preserving RF in the early post-transplant period are key to long-term GS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Irish W, Corral M, Ravindra K, Sudan D, Kreter B, Hebden H. Impact of Pre-Transplant Donor Renal Function on Graft Survival Following Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-pre-transplant-donor-renal-function-on-graft-survival-following-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
