Impact of mTOR and Calcineurin Inhibition on Lipid and Glucose Metabolism – 24 Month Assessment in De Novo Liver Transplant Recipients Treated with Everolimus and Tacrolimus
For the H2304 Investigators, Hamburg, Germany
Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A604
Immunosuppressants, particularly corticosteroids (CS) and calcineurin inhibitors used after liver transplantation (LTx) can adversely affect lipid metabolism. mTOR inhibition blocks insulin-stimulated lipoprotein lipase and can also result in dyslipidemia.
In the randomized, 24-month (M), open-label H2304 study, patients at one month post-LTx started EVR (C0 3-8ng/mL) plus reduced tacrolimus (C0 3-5ng/mL; rTAC) (N=245) or standard TAC (C0 6-10ng/mL; TAC-C) (N=241); patients from both arms received concomitant CS. The following metabolic parameters were analyzed at M12 and 24: blood levels of total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) and triglycerides (TG); incidence of new onset of diabetes mellitus (NODM); change in body weight; and incidence of cardiac events. NODM was identified by either adverse event reporting, fasting glucose measurement, HbA1c, or need for anti-diabetic medication.
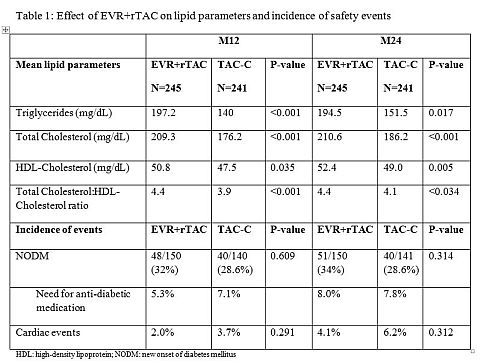
At M12 and 24, mean TC, TG and HDL levels were higher in the EVR+rTAC group compared to TAC-C (Table 1). Mean TC:HDL ratio remained below the American Heart Association-recommended threshold of 5:1 in both treatment groups. A higher proportion of patients received lipid-lowering agents (LLA) in the EVR+rTAC group (M12: 23.3% vs 17.8%; M24: 29.0% vs. 19.4%). TC levels ≥240mg/dL returned to normal levels in 13/19 (68.4%) EVR+rTAC patients by M12 following the initiation of LLA. Comparable proportions of patients developed NODM in both study arms. Patients in the EVR+rTAC group had a numerically smaller increase in mean body weight than patients receiving TAC-C (baseline-M12: 5.9kg vs. 8.2kg; -M24: 6.7kg vs. 9.5kg). The incidence of cardiac events, including ischemic heart disease and cardiac failure, was low in both groups.
Mean lipid parameters in the EVR+rTAC group stabilized after M12 in the range of normal to mildly elevated values. LLA can further help to manage persistent hyperlipidemia. The trend to lower weight gain with EVR+rTAC might be of interest in the longer term management of cardiovascular risk.
Fischer, L.: Grant/Research Support, Novartis, Astellas, Gilead. De Simone, P.: Grant/Research Support, Novartis. Saliba, F.: Other, Novartis, Advisory Committee or Review Panel, Astellas, Advisory Committee or Review Panel, Roche, Advisory Committee or Review Panel, Genzyme, Advisory Committee or Review Panel, Schering Plough, Speaking and Teaching, Gambro, Speaking and Teaching. Fung, J.: Grant/Research Support, Sanofi, Novartis. Dong, G.: Employee, Novartis. Lopez, P.: Employee, Novartis. Kohler, S.: Employee, Novartis. Junge, G.: Employee, Novartis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fischer L, Simone PDe, Saliba F, Fung J, Dong G, Lopez P, Kohler S, Junge G. Impact of mTOR and Calcineurin Inhibition on Lipid and Glucose Metabolism – 24 Month Assessment in De Novo Liver Transplant Recipients Treated with Everolimus and Tacrolimus [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-mtor-and-calcineurin-inhibition-on-lipid-and-glucose-metabolism-24-month-assessment-in-de-novo-liver-transplant-recipients-treated-with-everolimus-and-tacrolimus/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
