Impact of Integrase Inhibitor-Based Antiretroviral Regimen on Outcomes in HIV + Renal Transplant Recipients
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 447
Keywords: HIV virus, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Complications: Other
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:00pm-4:12pm
Presentation Time: 4:00pm-4:12pm
Location: Room 118-AB
Renal transplant in HIV+ patients (pts) is complicated by high rates of acute rejection (AR). Protease inhibitors (PIs) and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) have significant drug interactions with calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs). These interactions may contribute to a higher incidence of AR. The integrase strand inhibitor, raltegravir (RAL) does not interact with CNIs. The purpose of our study is to describe the effect of an RAL-based ARV regimen on outcomes including rejection, patient and allograft survival, CD4 count and infections.
Methods: Retrospective review of HIV+ transplant pts at our institution from 2004-2014, including pts reported in the HIV-TR multisite study (#AI-052748). Pts received induction with rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG) or basiliximab, tacrolimus or sirolimus, mycophenolate mofetil and corticosteroids.
| Raltegravir group (n=9) | PI-based or NNRTI-based group (n=24) | P value | |
| Recipient age | 46± 10.0 | 46.75± 6.6 | 0.85 |
| CD4 at transplant | 491.4± 211.5 | 485.2± 275.0 | 0.95 |
| African American | 1(11) | 13(54) | 0.05 |
| Caucasian | 3(33) | 9(38) | 1.00 |
| Hispanic | 3(33) | 1(4) | 0.05 |
| Other race | 2(22) | 1(4) | 0.17 |
| Male gender | 7(78) | 21(88) | 0.60 |
| HCV+ | 3(33) | 2(8) | 0.11 |
| Living donor | 3(33) | 5(21) | 0.65 |
| Deceased donor | 6(67) | 19(79) | 0.40 |
| Delayed graft function | 5(56) | 12(50) | 1.00 |
| Induction: Basiliximab | 1(11) | 13(54) | 0.05 |
| Induction: rATG | 8(89) | 8(33) | 0.007 |
| No induction | 0 | 3(13) | 0.54 |
| Length of follow-up | 2.1± 1.5 | 6.8± 2.2 | <.0001 |
| Rejection at 1 year | 1(11) | 6(25) | 0.642 |
| Rejection at 3 years | 1(11) | 8(33) | 0.384 |
| 1 year patient survival | 9(100) | 23(96) | 1.00 |
| 1 year graft survival | 9(100) | 22(92) | 1.00 |
| Overall graft survival at f/u | 9 (100) | 16(67) | 0.07 |
| Serious infections | 1.2±1.4 | 2.3±3.2 | 0.19 |
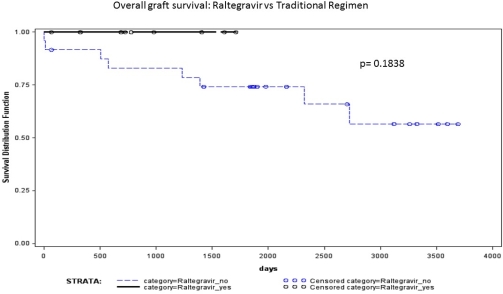
CD4 counts were lower at 2 years in the RAL pts (250±5 vs 368±163, p=0.002), with no difference in serious infections. AR and overall graft failure was lower in pts on RAL at any time post-transplant (p=0.12, 0.05 respectively).
The data suggests a trend towards reduced AR and improved graft survival in pts on RAL-based regimens, supporting the hypothesis that interactions between CNIs and traditional ARV regimens may lead to worse outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kershaw C, Rogers C, Pavlakis M, Tang H, Alonso C, Khwaja K, Evenson A, Raven K, Wong M. Impact of Integrase Inhibitor-Based Antiretroviral Regimen on Outcomes in HIV + Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-integrase-inhibitor-based-antiretroviral-regimen-on-outcomes-in-hiv-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
