Impact of Insulin Therapy in Pancreas Transplantation Donors on Graft Outcomes: An Analysis of the Optn/unos Database
1Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation Department, Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2Hepatobiliopancreatic and Liver Transplant Department, Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 3Endocrinology Department, Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 4Laboratori Experimental de Nefrologia I Trasplantament (LENIT), CRB CELLEX, Fundació Clínic, IDIBAPS, Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 5Urology Department, Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1228
Keywords: Donation, Insulin, Kidney/pancreas transplantation, Pancreas transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Pancreas » Pancreas and Islet: All Topics
Session Information
Session Name: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Hyperglycemia requiring insulin treatment is frequent in critically ill patients and potential pancreas donors. Information on the impact of donor insulin use on pancreas outcomes is scarce. Thus, we explored the influence of donor insulin use on recipient and pancreas graft survival.
*Methods: Retrospective study with 12841 pancreas recipients (either simultaneous pancreas-kidney, pancreas after kidney or pancreas alone) from the OPTN/UNOS registry performed between 2000 and 2017. Multivisceral recipients other than simultaneous pancreas-kidney, those transplants from a donor < 30 kg and recipients with diabetes other than type 1 or 2 were excluded. Insulin donor requirements were defined as the need for any dose of insulin within 24 hours prior to donation.
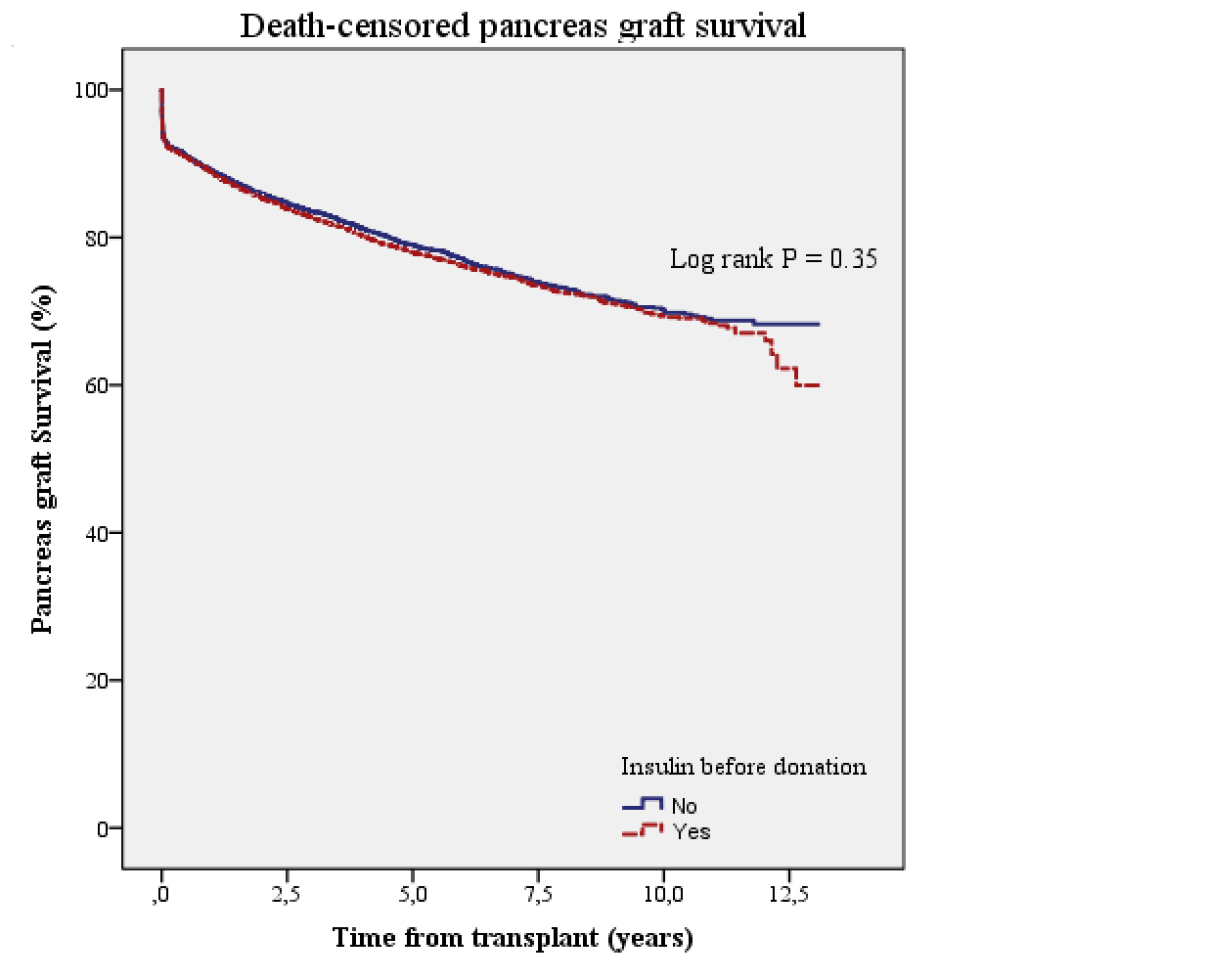
*Results: A total of 7765 (60%) patients received a pancreas from a donor with insulin requirements. Pancreas graft survival (death-censored) at 1 year was similar between those who received an insulin-requiring donor and the remaining (89% vs 89%, P > 0.05), as well as at 5 and 10 years (78% and 69% vs 79% and 70%, respectively, P = 0.35)(Figure). Donor insulin therapy was not associated neither with an increased risk of recipient death (HR 0.93 [95% CI 0.80-1.07], P = 0.29) nor pancreas graft failure (HR 1.08 [95% CI 0.99-1.17], P = 0.09).
*Conclusions: Insulin requirements in a potential pancreas donor is not associated, per se, with an impaired pancreas graft and patient survival. Thus, donors who require insulin therapy may be suitable for pancreas transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Montagud-Marrahi E, Ausania F, Fundora Y, Amor A, Esmatjes E, Ferrer J, Revuelta I, Cucchiari D, Rovira J, Musquera M, Fondevila C, Diekmann F, Ventura-Aguiar P. Impact of Insulin Therapy in Pancreas Transplantation Donors on Graft Outcomes: An Analysis of the Optn/unos Database [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-insulin-therapy-in-pancreas-transplantation-donors-on-graft-outcomes-an-analysis-of-the-optn-unos-database/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress