Impact of Functional Status on Outcomes of Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation: Risks and Opportunities for Patient Benefit
1Department of Medicine, Saint Louis University, Saint Louis, MO, 2Washington Univ, Seattle, WA, 3Georgetown Univ, Washington, DC, 4Saint Louis University, Saint Louis, MO, 5Univ of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, 6Weill Cornell, New York, NY, 7Univ of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, 8SRTR, Minneapolis, MN, 9Emory, Atlanta, GA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 399
Keywords: Elderly patients, Outcome, Pancreas transplantation, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics I
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:39pm-3:51pm
Presentation Time: 3:39pm-3:51pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The impact of functional status on survival among simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant (SPKT) candidates and recipients is not well described.
*Methods: We examined national Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients data for 16,822 patients listed for SPKT in the US. (2006-2019). Functional status was categorized by center-reported Karnofsky score as: normal (80-100); cares for self (70); requires assistance (50-60); or disabled (10-40). We assessed associations of functional status at listing and transplant with subsequent patient survival, adjusted for baseline patient and transplant factors. We also explored time-dependent associations (adjusted hazard ratio, aHR) of SPKT with survival risk after listing compared with continued waiting in each functional status group by multivariable Cox regression, partitioned by time <30d and >30d of SPKT.
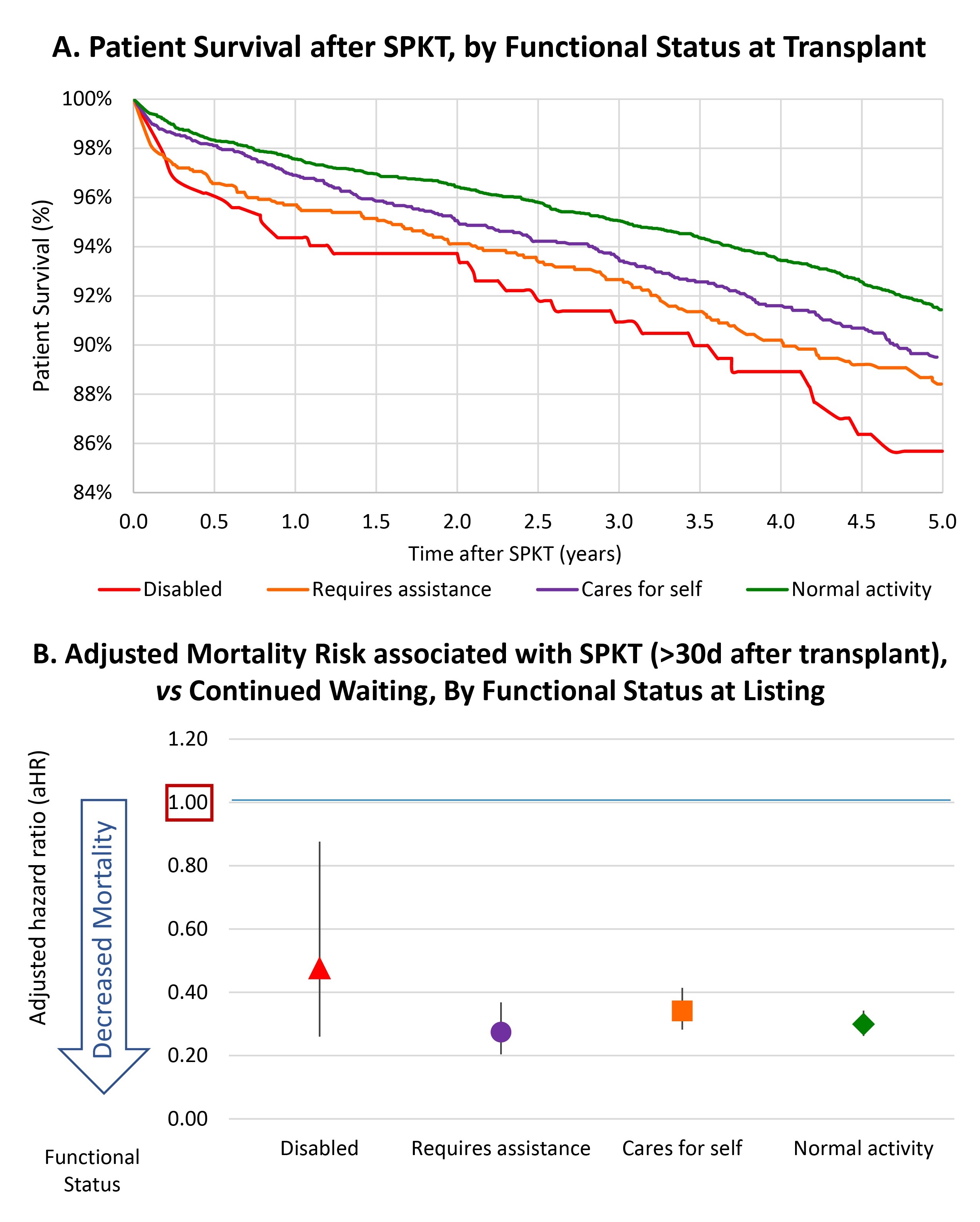
*Results: Distributions of functional status among candidates and recipients, respectively were: normal, 62.0% and 57.8%; cares for self, 23.5% and 24.7%; requires assistance, 12.4% and 14.2%; and disabled, 2.1% and 3.3%. Compared with normal activity, there was a graded decline in survival after listing and after transplant (Fig 1A) with lower functional levels. These associations persisted with covariate adjustment, such that caring for self (aHR 1.18, P=0.05), requiring assistance (aHR 1.31, P<0.001), and disability (aHR 1.55, P<0.001) were associated with graded increases in mortality after SPKT. Compared with waiting, SPKT was associated with ~2-fold mortality risk within 30 days of transplant. However, beyond 30 days, SPKT was associated with reduced mortality compared with waiting across functional status levels, from 52% among disabled (aHR 0.48) to 70% in those with normal activity (aHR 0.70) (Fig 1B).
*Conclusions: While lower center-reported functional status is associated with increased mortality risk among SPKT candidates and recipients, SPKT provides substantial long-term survival benefit across functional status levels. These data suggest need for pre- and posttransplant rehabilitation to reduce frailty, while supporting SPKT opportunities for all patients who can benefit.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lentine K, Alhamad T, Cooper M, Zhang Z, Woodside K, Dadhania D, Chang S, Axelrod D, Schnitzler M, Ouseph R, Snyder J, Kasiske B, Parsons R. Impact of Functional Status on Outcomes of Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation: Risks and Opportunities for Patient Benefit [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-functional-status-on-outcomes-of-simultaneous-pancreas-kidney-transplantation-risks-and-opportunities-for-patient-benefit/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress