Impact of Electronic Donor Referral Technology on Deceased Donor Referrals
1Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD, 2Yale, New Haven, CT, 3Transplant Connect, Santa Monica, CA, 4Southwest Transplant Alliance, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 689
Keywords: Allocation, Donation
Topic: Clinical Science » Public Policy » Non-Organ Specific: Public Policy & Allocation
Session Information
Session Name: Non-Organ Specific: Public Policy & Allocation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Hospitals likely fail to refer many medically eligible potential deceased donors to OPOs. As such, increasing eligible referrals may increase the donor pool. We hypothesized that implementation of iReferralSM, an automated and electronic referral platform, would be an effective method of circumventing the challenges faced with the current phone-based referral system.
*Methods: To better understand the impact of the iReferralSM system on referrals, we conducted a retrospective study of all deceased donor referrals (n=1409) to three Texas hospitals January 2016 – August 2020. We used Poisson regression to analyze changes in the number of referrals following deployment of the iReferralSM system in October 2018, overall and for various subgroups, adjusting for seasonality and secular trends.
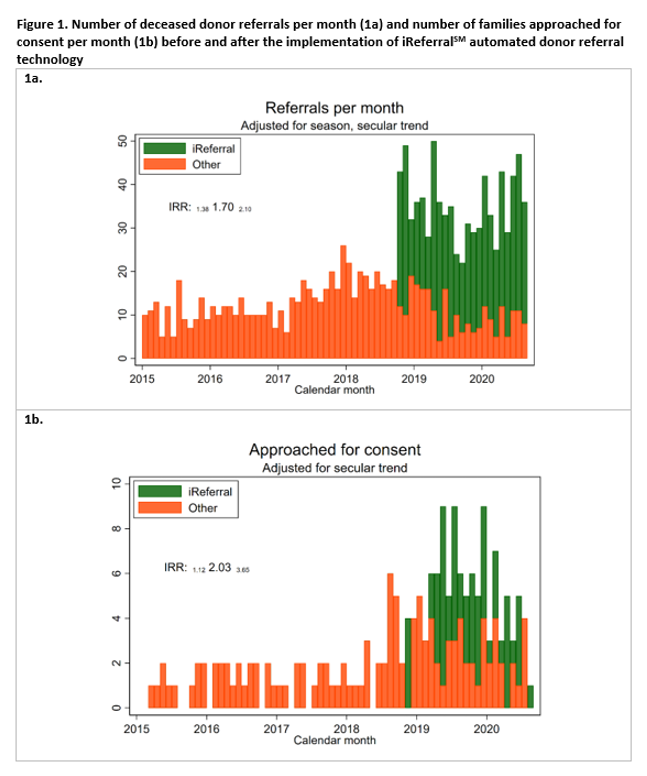
*Results: After implementation of iReferralSM, the number of patient referrals increased from median (IQR) 14 (12-18) to 36 (31-43) (p<0.001), representing a 70% total increase per month (IRR 1.38 1.70 2.10 p<0.001) (Figure 1). This increase was seen across various subgroups including patients <50 (IRR 1.07 1.73 2.81 p=0.02) and >50 years old (IRR 1.36 1.72 2.16 p<0.001), and brain dead patients (IRR 1.43 1.76 2.16 p<0.001). Median (IQR) hours from admission to referral decreased from 60 (13-157) to 30 (7-152) (p<0.001). The number of patients whose families were approached for consent doubled (IRR 1.12 2.03 3.65 p=0.02). The number of donors per month was 26% higher than pre-iReferralSM, though the difference was not statistically significant (p=0.3).
*Conclusions: After the implementation of an automated and electronic donor referral, the rate of deceased donor referrals increased substantially, and the number of patients whose families were approached for consent doubled. Automating the process at these key upstream steps in the deceased donor process may increase hospital and OPO efficiency and donor referrals.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Boyarsky B, DiRito JR, Vanterpool K, Piano J, Liu W, Hewlett J, Trahan C, Segev D, Levan M, Massie A, Niles P. Impact of Electronic Donor Referral Technology on Deceased Donor Referrals [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-electronic-donor-referral-technology-on-deceased-donor-referrals/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress