Impact of Covid-19 Infection on Tacrolimus Levels in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, IL
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: LB 59
Keywords: Immunosuppression
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » COVID-19
Session Information
Session Name: COVID-19
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Immunocompromised patients are considered to be at high-risk for infection with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). There have been observations within the transplant community that patients infected with COVID-19 have increased tacrolimus trough levels. A common presenting symptom of COVID-19 is diarrhea, which is a risk factor for increased tacrolimus levels. COVID-19 treatment often includes remdesivir, a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor that may also lead to increased tacrolimus levels. The study purpose was to determine the effect of COVID-19 infection and associated treatments on tacrolimus levels.
*Methods: This retrospective chart review evaluated all solid organ transplant recipients admitted inpatient to the study institution within 14 days of a positive COVID-19 PCR test. Patients were excluded if they were treated outpatient, were not on tacrolimus, or were initially treated at an outside hospital. Patients were considered to have a clinically significant increased tacrolimus trough level if their admission level was 20% or greater than their baseline. Baseline levels were defined as the most recent trough level on a consistent dose per pharmacist clinical judgement. A logistic regression was performed to evaluate potential risk factors for elevated levels.
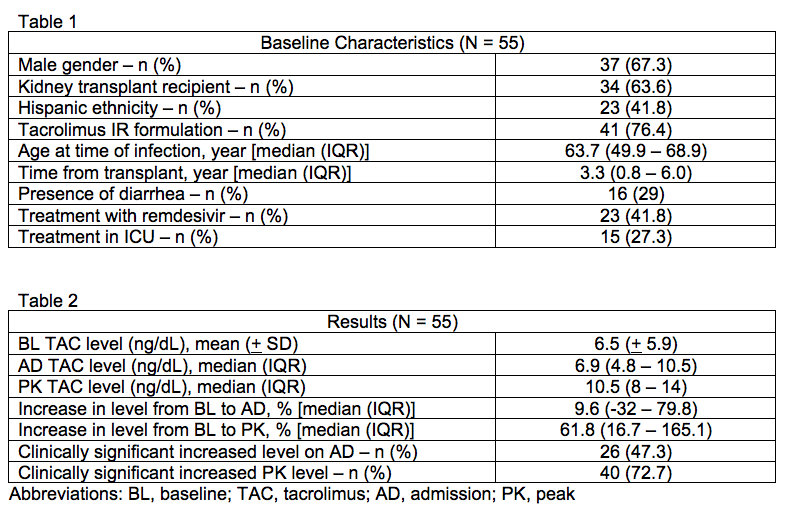
*Results: A total of 55 patients met inclusion criteria from March 1, 2020 to December 26, 2020. Baseline characteristics are listed in Table 1. The majority of patients were male (67.3%), kidney transplant recipients (63.6%), and Hispanic ethnicity (41.8%). A clinically significant increase from baseline was observed in 47.3% of patients on admission. When comparing baseline level to peak trough level, 72.7% of patients had a clinically significant increase (Table 2). Transplant type, tacrolimus formulation, presence of diarrhea, and treatment with remdesivir were not associated with increased tacrolimus trough levels.
*Conclusions: In transplant patients admitted with COVID-19, 43.7% of patients and 72.7% had increased trough levels on admission and peak trough levels greater than 20% of baseline, respectively. Potential risk factors for elevated levels, including presence of diarrhea and treatment with remdesivir, did not significantly increase the risk of elevated tacrolimus levels. These findings suggest that infection with COVID-19 may be an independent risk factor for increased tacrolimus levels, but will require further investigation to determine the full effect. Increased tacrolimus trough level monitoring should be considered in solid organ transplant recipients infected with COVID-19 to avoid toxicities associated with supratherapeutic levels.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Heagler K, Tejani K, Sanchez S. Impact of Covid-19 Infection on Tacrolimus Levels in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-covid-19-infection-on-tacrolimus-levels-in-solid-organ-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress