Impact of CHA2DS2-VASc Score on Postoperative Mortality Following Kidney Transplant
1Surgery, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL, 2Surgery, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 32
Keywords: Allocation, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 5, 2021
Session Time: 4:30pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:55pm-5:00pm
Presentation Time: 4:55pm-5:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: This study aimed to assess the correlation between CHA2DS2-VASc score and postoperative kidney transplant survival. The conditions captured in the CHA2DS2-VASc score are commonly found in patients undergoing kidney transplant and are the leading causes for mortality in this patient population.
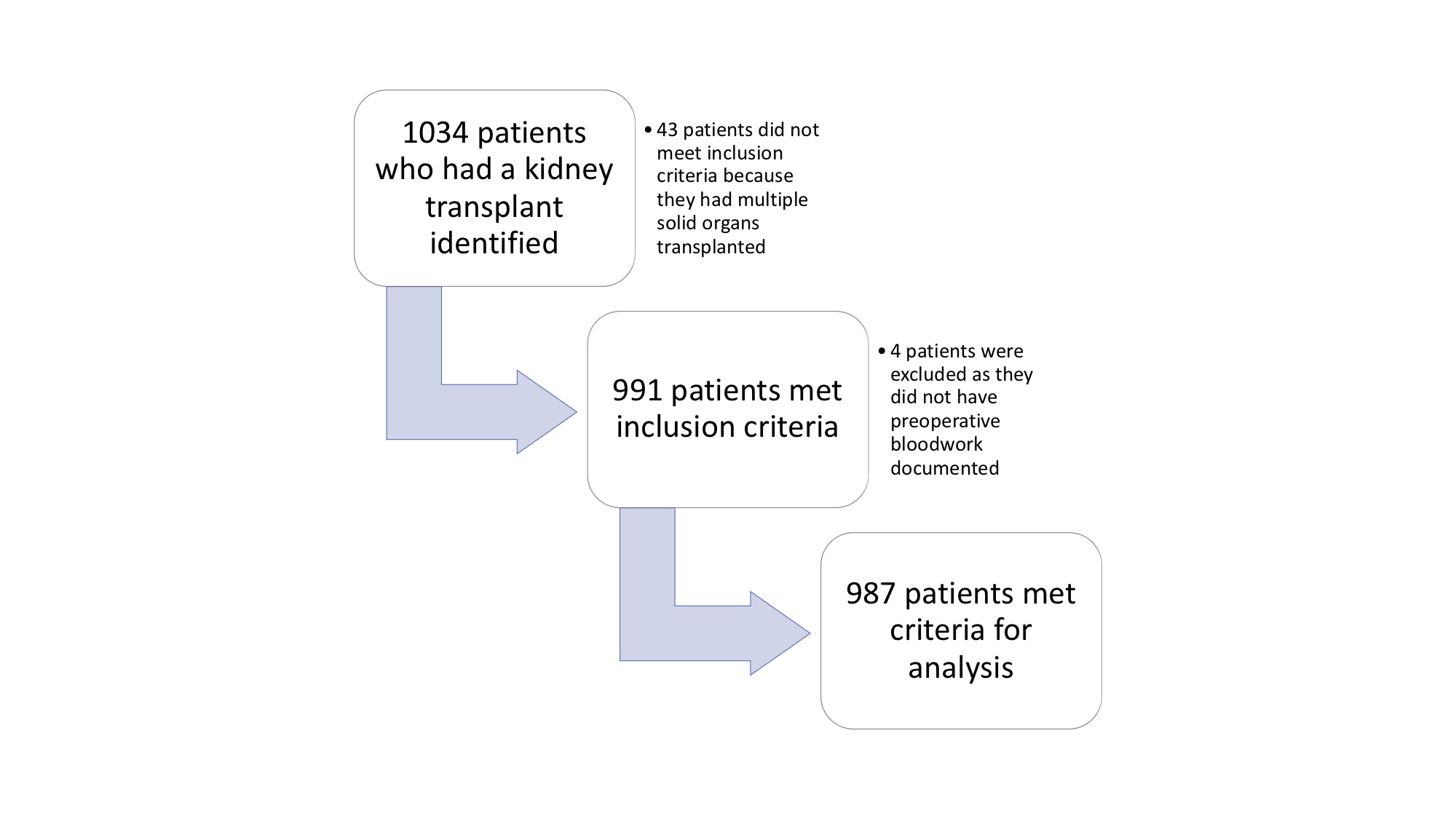
*Methods: A retrospective chart review of all patients over 18 undergoing kindey transplant between 2009 and 2019 at a single institution was conducted. 1034 patients were identified, and after inclusion and exclusion criteria were identified, 987 patients were analyzed (Figure 1).
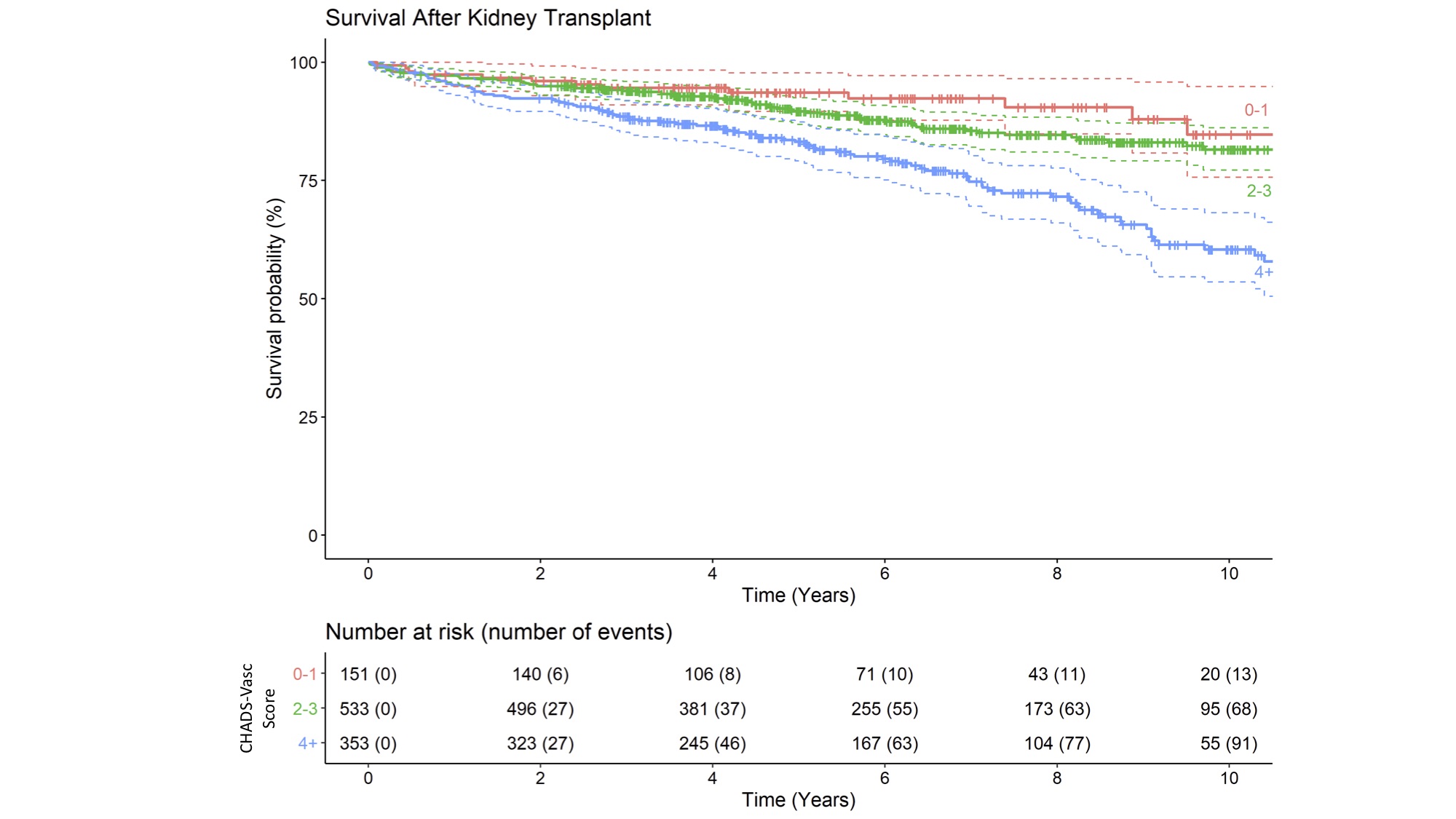
*Results: 987 patients were stratified into three groups based on CHA2DS2-VASc score (0-1, 2-3, 4+). Not surprisingly, survival probability decreased over time following kidney transplantation. Median follow-up was 5.7 years (IQR 3.7-8.7). At one year there was a 94% survival rate, which decreased to 86% survival at 6 years. When comparing groups, the highest (4+) score group had at least a 64% higher risk in mortality compared to the lowest score group (HR 2.88, 95% CI 1.64-5.04, p<0.001). When controlling for the other components of the score, diabetes (HR 1.94; 95%CI 1.32-2.8, p<0.001) and peripheral vascular disease (HR 1.63; 95%CI 1.15-2.3, p=0.006) were associated with higher mortality. Age 65-74 (HR 1.71; 95%CI 1.21-2.4, p=0.003) was associated with higher mortality than age <65.
*Conclusions: A CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4+ is associated with increased mortality following kidney transplantation, with diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and older age the three independent contributory components. Current allocation algorithms incorporate age and diabetes, but inclusion of either CHA2DS2-VASc score or presence of peripheral vascular disease may help more appropriately allocate organs. This knowledge can be beneficial moving forward as transplant teams judge which donor offers to accept for an increasingly older population with more comorbidities.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Klein J, Rangel M, Spigel Z, Hollinger E, Olaitan D, Hertl M, Chan E. Impact of CHA2DS2-VASc Score on Postoperative Mortality Following Kidney Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-cha2ds2-vasc-score-on-postoperative-mortality-following-kidney-transplant/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress