Impact of Carbapenem Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Blood Stream Infection in Solid Organ Transplantation
Department of Infectious Disease, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Department of Clinical Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 504
Introduction. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKp) infections are an increasing threat to solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients.
Methods. SOT recipients with carbapenem-resistant (CR) vs. carbapenem-susceptible (CS) K. pneumoniae blood stream infection (BSI) were compared in a retrospective cohort study between 2006–2012. A Kaplan-Meier curve with log-rank statistics was used to compare all-cause mortality (JMP 9.0, SAS, NC).
Results. We identified 84 episodes of K. pneumoniae BSI in 65 SOT recipients, including 19 kidney, 23 liver, 3 heart, 10 lung, 1 intestinal, 1 pancreas, and 8 multi-visceral transplants. 23/84 (27%) episodes of BSI identified in 19 patients were due to CRKp. 5/19 (26%) of these patients had been previously infected or colonized by CRKp at any site. When comparing episodes of CRKp with CSKp BSI, infection occurred sooner after transplant (median 73 d vs. 316 d, p 0.009), and 30-day all-cause mortality was significantly higher (43% vs. 15%, p = 0.005). However, the percentage of patients receiving in vitro effective antibiotic treatment within 48 hrs was not significantly different between CRKp and CSKp BSI (74% vs. 88%, p 0.09). Of the CRKp BSI episodes, 15 (65%) were treated with a combination of at least two antibiotics to which the isolate was susceptible in vitro, and 8 (35%) were treated with a single antimicrobial agent (3 colistin, 3 tigecycline, and 2 aminoglycoside). When limiting 30-day survival analysis to the first episode of K. pneumoniae BSI per patient, carbapenem resistance remained highly significantly associated with death (see figure, p 0.01).
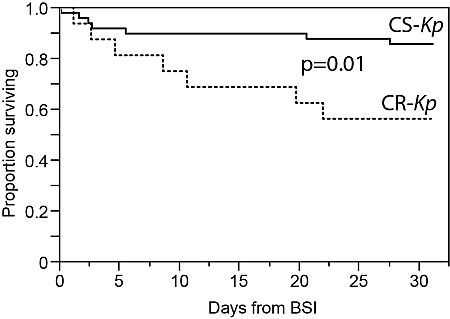
Conclusions. A large proportion of recent K. pneumoniae BSI in SOT recipients was caused by CRKp, which tended to occur earlier after transplantation. All-cause mortality associated with CRKp BSI among SOT recipients is higher than CSKp BSI despite early initiation of active antibiotics. Improved therapeutic and preventive measures are needed to confront this emerging infection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cober E, Brizendine K, Richter S, Koval C, Duin DVan. Impact of Carbapenem Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Blood Stream Infection in Solid Organ Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-carbapenem-resistance-in-klebsiella-pneumoniae-blood-stream-infection-in-solid-organ-transplantation/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
