IL-2 Antagonist Induction Therapy Preserves Renal Function in Liver Transplant Recipients
Pharmacy, MUSC, Charleston, SC
Transplant, MUSC, Charleston, SC
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D1696
Background: Studies have produced varying results regarding whether IL-2 antagonist induction improves outcomes, including renal function and patient and graft survival in liver transplantation. This analysis seeks to evaluate the effect of IL-2 antagonist induction on patient outcomes.
Methods: This was a large-scale longitudinal cohort study of all liver transplants at our institution from Jan 2000 – June 2011. Patients were excluded if they were <18 years old, multi-organ transplants, or experienced graft loss or death within the first month. Patients were divided into 2 groups based on whether they received IL-2 antagonist induction. Renal function was estimated using the MDRD equation, and the change in renal function from baseline was assessed by calculating a slope of MDRD over time.
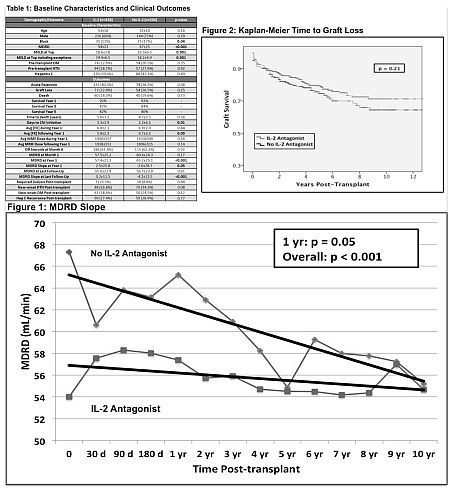
Results: 635 transplants occurred during this period; 532 were included in the analysis (mean follow-up 4.8 yrs). Baseline demographics and outcome data are in Table 1. 328 patients (62%) received IL-2 antagonist induction. The IL-2 group had a lower MDRD and higher MELD at baseline. The MDRD slope showed that renal function was better preserved in the IL-2 group at both 1 year and at last follow-up (p=0.05 and p<0.001, respectively; Table 1 & Figure 1). There was no difference between the two groups for acute rejection (p=0.36), hepatitis C recurrence (p=0.77), graft loss (p=0.25), or death (p=0.73) (Table 1 & Figure 2). While there was a difference in mean FK level after yr 1, this variable was not shown to independently affect MDRD slope in linear regression analysis, while IL-2 antagonist induction was shown to independently affect the MDRD slope.
Conclusions: IL-2 antagonist induction provides a renal-sparing benefit in liver transplant recipients while maintaining equivalent rates of acute rejection, hepatitis C recurrence, and graft and patient survival. These results should be validated in large-scale prospective clinical trials to further evaluate its utility in the liver transplant population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mardis A, Meadows H, Taber D, Pilch N, Fleming J, Jordan C, Morbitzer K, Makowski C, McGillicuddy J, Bratton C, Chavin K, Baliga P. IL-2 Antagonist Induction Therapy Preserves Renal Function in Liver Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/il-2-antagonist-induction-therapy-preserves-renal-function-in-liver-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
