Identification of Relevant Renal Transplant Patient Reported Symptoms That Could Be Used for New Patient Reported Outcome Development
I. Purnajo1, J. Beaumont1, M. Polinsky2, E. Alemao2, M. J. Everly1
1Terasaki Research Institute, Los Angeles, CA, 2Bristol Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C113
Keywords: Quality of life
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Psychosocial
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: We analyzed post-transplant health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and symptom experience captured longitudinally in the belatacept vs. cyclosporine (BENEFIT and BENEFIT-EXT) trial cohorts to identify symptoms that strongly correlate with HRQoL and could be used to create a new patient reported symptom index for renal transplantation.
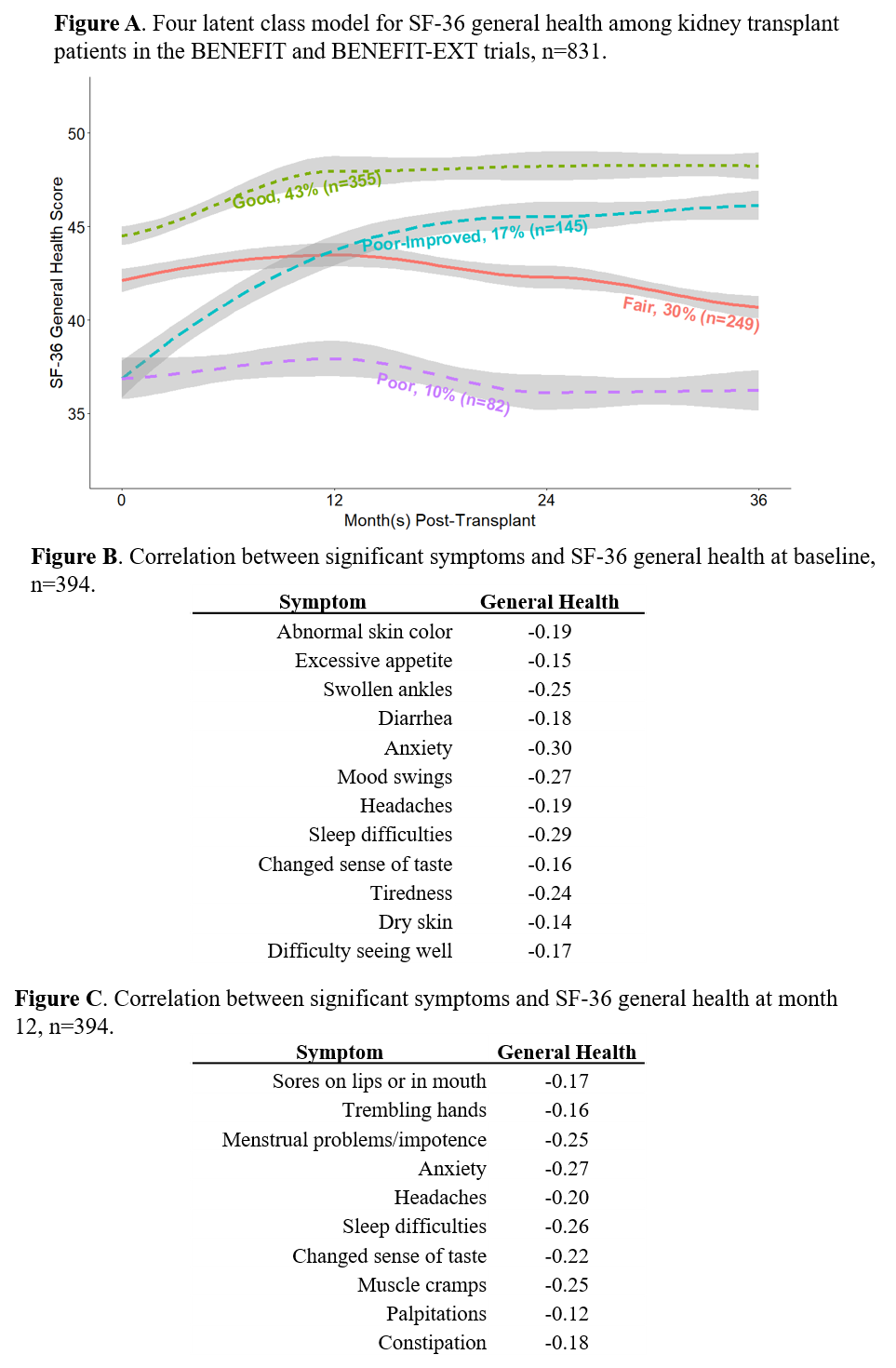
*Methods: SF-36 (HRQoL) and MTSODS-59R (symptom distress) surveys were collected at baseline, 12, 24, and 36 months post-transplant; however, data for MTSODS-59R were collected only among participants in the BENEFIT trial. Latent class mixed effect modeling was conducted after excluding those with graft failure and drug discontinuation before the 1st year (n=831), revealing four latent classes for general health: good, fair, poor-improved, and poor (Figure A). Bivariate and multivariate analyses were conducted to examine the association between general health latent classes and each symptom at baseline and 12 months post-transplant (n=394). For both the baseline and 12 month analyses, symptoms that were statistically significant (p<0.05) in the bivariate analysis were entered into a multivariable regression model. Correlation between each significant symptom and general health was also conducted at baseline and month 12.
*Results: Twelve baseline symptoms were found to be associated with SF-36 general health subscale class: anxiety, abnormal skin color, mood swings, sleep difficulties, tiredness, headaches, swollen ankles, difficulty seeing well, diarrhea, changed sense of taste, dry skin, and excessive appetite (Figure B). Ten symptoms at month 12 were found to be associated with SF-36 general health subscale class: muscle cramps, changed sense of taste, headaches, sleep difficulties, constipation, anxiety, sores on lips or in mouth, trembling hands, palpitations, and menstrual problems/impotence (Figure C).
*Conclusions: Collectively, this symptom list accounts for both the underlying kidney disease and changes due to transplant and serve as a basis to develop a new transplant related symptom measure that could correlate with a patient’s quality of life.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Purnajo I, Beaumont J, Polinsky M, Alemao E, Everly MJ. Identification of Relevant Renal Transplant Patient Reported Symptoms That Could Be Used for New Patient Reported Outcome Development [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/identification-of-relevant-renal-transplant-patient-reported-symptoms-that-could-be-used-for-new-patient-reported-outcome-development/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress