HLA-DR Matching Improves Immunologic Outcomes in Elderly Kidney Transplant Recipients
Nephrology, Charité
Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D60
Keywords: Elderly patients, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Donor Specific Antibodies/Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
BACKGROUND: The Eurotransplant senior program (ESP) neglects HLA matching for elderly (>65y) KTR. Only few data exist regarding the influence of HLA-DR-matching on immunologic outcomes.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: This retrospective long-term observational study included 205 elderly KTR between 2006 and 2014. Standard immunosuppression including induction therapy (IL2-R) was administered in all patients (pts). Allograft biopsies were performed for clinically suspected rejections. Follow-up DSA analysis was routinely performed. Data analysis included patient and graft survival, biopsy proven rejections (TCMR and ABMR) and development of de novo DSA. Outcome data were assessed over maximal 8 years.
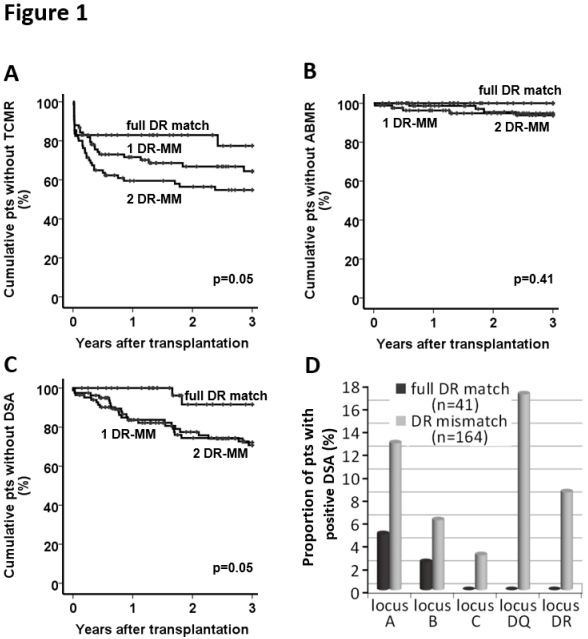
RESULTS: 41 pts had full HLA-DR-match, 83 pts 1 DR-mismatch (DR-MM) and 81 pts 2 DR-MM. Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. Full HLA-DR-match showed significantly lower predicted rate of TCMR episodes than 1 DR-MM or 2 DR-MM (23%, 36%, 45% respectively) and less development of de-novo DSA. In addition full-DR-match also was associated with significantly less development of other types of de novo DSA (Figure 1). Only 4% of KTR developed an ABMR. Differences in patient and graft survival were not significant.
CONCLUSION: HLA-DR mismatches are a risk factor for rejection and development of de novo DSA. DR matching might significantly improve immunologic outcomes in elderly patients.
| Patient characteristics | all; n=205 | full DR-match; n=41 | DR mismatch; n=164 | p |
| Mean follow up, years (SD) | 3.6 (3.3) | 2.5 (1.7) | 3.8 (2.4) | <0.001 |
| Mean recipient age, years (SD) | 69 (4) | 70 (3) | 69 (3) | 0.016 |
| Mean donor age, years (SD) | 69 (9) | 67 (10) | 70 (9) | 0.228 |
| Male, n | 119 (58%) | 26 (63%) | 93 (57%) | 0.483 |
| Living donor, n | 21 (10%) | 7 (17%) | 14 (9%) | 0.145 |
| Prior kidney transplantation, n | 8 (4%) | 4 (10%) | 4 (2.4%) | 0.053 |
| Median time on dialysis, months (IQR) | 44 (25-62) | 44 (26-60) | 44 (25-62) | 0.794 |
| Median cold ischemia time, hours (IQR) † | 10 (8-12) | 11 (8-14) | 10 (7-12) | 0.608 |
| Median HLA-mismatches (IQR) | 4 (3-5) | 2 (1-3) | 5 (4-5) | <0.001 |
| † in patients with deceased donors (n=183) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Halleck F, Khadzhynov D, Liefeldt L, Glander P, Bamoulid J, Kreimer S, Lehner L, Budde K, Staeck O. HLA-DR Matching Improves Immunologic Outcomes in Elderly Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/hla-dr-matching-improves-immunologic-outcomes-in-elderly-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
