HIV, HBV, and HCV Screening with NAT and Serology in the OPO Setting
1UMass Memorial Medical Center, Worcester, MA
2Northwestern University, Chicago, IL.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 564
Keywords: Donation, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HIV virus
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: New Frontiers in HIV and Hepatitis
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Room 4C-3
Background:
In December 2014, the Organ Procurement & Transplantation Network updated policy to mandate screening with nucleic acid tests (NAT) for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in all donors and HIV NAT in increased risk donors. Given the shorter window period associated with NAT, infections will be detected earlier by NAT than serology. The actual number of additional infections detected by NAT has not been reported.
Methods:
HIV, HBV and HCV screening results of individuals referred for evaluation of deceased organ donation from 2004-2016 were obtained from 23 participating Organ Procurement Organizations (OPO). REDCap was used for data collection. Funding was provided by Mendez National Institute of Transplantation Foundation grant.
Results:
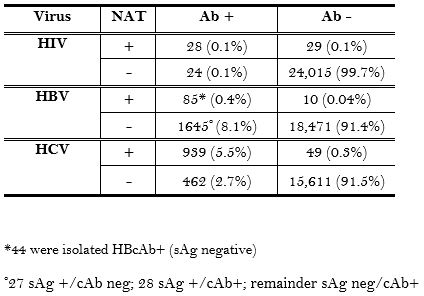
36,429 potential organ donor screening labs were reviewed. NAT detected 29 (0.1%), 10 (0.04%), and 49 (0.3%) additional HIV, HBV, and HCV infections, respectively, in seronegative referrals. There were 2107 referrals that were seropositive for either HBV or HCV, but were not viremic by NAT. 83.8% of the total population became organ donors.
Conclusions:
As expected, NAT detected infections that serology did not, especially in the case of HCV. Importantly, there are many seropositive, NAT negative donors that should be safe to use in certain recipients, especially the HCV Ab+/NAT- donors. The effect of these tests on utilization will be evaluated.
CITATION INFORMATION: Theodoropoulos N., Ison M. HIV, HBV, and HCV Screening with NAT and Serology in the OPO Setting Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Theodoropoulos N, Ison M. HIV, HBV, and HCV Screening with NAT and Serology in the OPO Setting [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/hiv-hbv-and-hcv-screening-with-nat-and-serology-in-the-opo-setting/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress