High GFR in Kidney Donors is Associated with Increased Risk of Proteinuria and Diabetes
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C62
Keywords: Donation, Kidney transplantation, Proteinuria
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Donor Selection / Management Issues
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Measured glomerular filtration rate (GFR) has been part of the donor evaluation to rule out low GFR donors from taking undue risk for ESRD. We hypothesize that high GFR patients may be at risk of development of adverse kidney outcomes after donation.
Methods: Between 1963-2001, 1097 donors had creatinine clearance at our institution. 929 had post-donation proteinuria status assessed. The effect of GFR on proteinuria was evaluated using a multivariate Cox proportional hazards, adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, year of donation, smoking status, donor type (related vs. unrelated), and whether recipient was diabetic. GFR was fit as a nonlinear effect based on examination of penalized splines, and knots were fit at 90 and 150 ml/min (25% had a GFR <90, 6.5% >150). Hazard ratio for GFR relative to 90 ml/min was based on the multivariate Cox model.
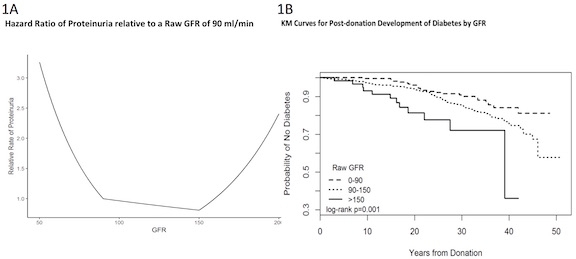
Results: Proteinuria risk increases with pre-donation GFR > 150 ml / min (Figure 1A). In the adjusted model (Table 1), for every 10 ml / min above 150 ml / min there was a 28.8% increased risk of proteinuria. High GFR (>150) donors were also at an increased risk of diabetes development following donation (Figure 1B).
Conclusions: Risk of proteinuria after kidney donation increases below 90 ml / min and above 150 ml / min as determined by timed creatinine clearance pre-donation. Donors with >150 ml / min had increased risk of development of diabetes post donation.
| Estimate | CI low | CI high | p.value | |
| GFR 10 ml / min >150 ml/min | 1.288 | 1.018 | 1.630 | 0.035 |
| Age | 1.009 | 0.989 | 1.029 | 0.365 |
| Male | 1.645 | 1.036 | 2.613 | 0.035 |
| BMI | 1.095 | 1.036 | 1.157 | 0.001 |
| Year of donation | 1.070 | 1.038 | 1.103 | 0.000 |
| LURD | 0.827 | 0.305 | 2.245 | 0.710 |
| DM in recipient | 0.636 | 0.406 | 0.996 | 0.048 |
| Smoking | 1.405 | 0.950 | 2.079 | 0.089 |
| White | 0.364 | 0.176 | 0.751 | 0.006 |
CITATION INFORMATION: Keys D., Riad S., Vakil V., Jackson S., Berglund D., Matas A. High GFR in Kidney Donors is Associated with Increased Risk of Proteinuria and Diabetes Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Keys D, Riad S, Vakil V, Jackson S, Berglund D, Matas A. High GFR in Kidney Donors is Associated with Increased Risk of Proteinuria and Diabetes [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/high-gfr-in-kidney-donors-is-associated-with-increased-risk-of-proteinuria-and-diabetes/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress