Health Utilities in Pediatric Liver Transplant Recipients
Pediatrics, Northwestern U, Chicago.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D193
Keywords: Economics, Outcome, Quality of life, Resource utilization
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Liver: Pediatrics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Health Utilities (HU) are preference based measures of health states required for cost effectiveness studies. We measured HU and health related quality of life (HRQOL) in pediatric liver transplant (LT) recipients.
Methods: A convenience sample of pediatric LT recipients ≥7yrs old were surveyed from 10/11-6/14 . Direct HU were assessed in 48 adolescents ≥12 yrs using the Standard Gamble (SG) and Time Trade Off (TTO) techniques. Indirect HU were measured using self-report by Health Utility Index 3(HUI) for subjects ≥12 yrs and the Child Health Utility Index 9D (CHU9D) for ≥7 yrs. HRQOL was self-reported using the PedsQL™ Generic Core (GC) Scale and Transplant Module (TM). Parents completed HU and HRQOL measures for their children regardless of age. “Ideal health” was defined as: normal transaminases, monotherapy, lack of chronic kidney disease, rejection and biliary obstruction. Mann-Whitney test and Spearman correlations were used to assess for significance between variables and HU and HRQOL.
Results: 108 subjects(44% male;73% Caucasian; 47% biliary atresia;35% living donor; 40% Medicaid) participated. Mean age at survey was 13.1±3.3 yrs and time from transplant was 8.9±4.9 yrs. 58% were on monotherapy, 25 had acute rejection in the last 3 yrs and 17 had a biliary obstruction in the last 5 yrs. 30/108 (28%) met criteria for “ideal health”. HU of various health states are shown in the table.
Direct HU was significantly higher by SG in subjects transplanted for biliary atresia and lower by TTO in those with rejection (p<0.05). Indirect HU was lower in Hispanics by self-report using HUI (p<0.05). No other medical/demographic variables including 'ideal health' reached significance.
SG and TTO correlated with each other (p<0.005) but not with indirect measures. Parents and children's indirect HU scores correlated well.(p<0.001) Significant correlation was noted among self-reported indirect HU and all subscales of PedsQL™ GC Scales (parent & self-report, p<0.005). Parent reported CHU9D correlated with patient and parent reported TM total scores (p<0.005).
Summary: In the largest report of HU in pediatric LT recipients, the availability of HU scores for health states including, 'ideal health” will inform future cost effectiveness studies.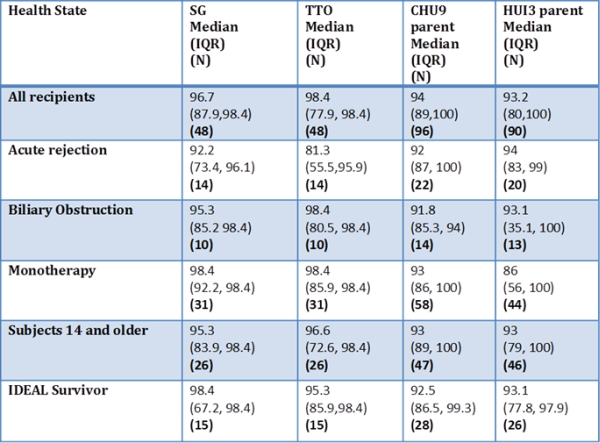
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mohammad S, Bharij A, Neighbors K, Alonso E. Health Utilities in Pediatric Liver Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/health-utilities-in-pediatric-liver-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
